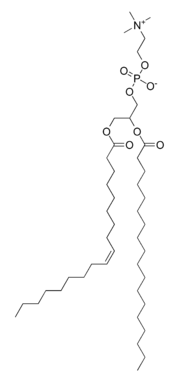
Phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid in lecithin.
Lecithin is mostly a mixture of glycolipids, triglycerides, and phospholipids (e.g., phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylinositol). However, in biochemistry, lecithin is usually used as a synonym for pure phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid that is the major component of a phosphatide fraction, which may be isolated from either egg yolk (in Greek lekithos—λεκιθος) or soy beans from which it is mechanically or chemically extracted using hexane.
Lecithin is commercially available in high purity as a food supplement and for medical uses. It is especially used by vegetarians as a meat supplement.
[ edit]In biology
edit]In biology
Phosphatidylcholine is an important component of the mucus layer or mucosa in the large intestine. This mucus layer forms the  mucosal barrier, protecting the large intestine from attacks from colonic commensal bacteria
mucosal barrier, protecting the large intestine from attacks from colonic commensal bacteria  [1]. Patients suffering from ulcerative colitis have a disturbed mucosal barrier, and the mucus layers in their large intestines exhibit lower levels of phosphatidylcholine than that of healthy people.
[1]. Patients suffering from ulcerative colitis have a disturbed mucosal barrier, and the mucus layers in their large intestines exhibit lower levels of phosphatidylcholine than that of healthy people.
[ edit]As a food additive
edit]As a food additive
Lecithin is regarded as a well-tolerated and non-toxic surfactant. It is approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration for human consumption with the status "Generally Recognized As Safe." Lecithin is an integral part of cell membranes, and can be totally metabolized, so it is virtually non-toxic to humans. Other emulsifiers can only be excreted via the kidneys.
Lecithin is used commercially in substances requiring a natural emulsifier and/or lubricant, from pharmaceuticals to protective coverings. For example, lecithin is the emulsifier that keeps cocoa and cocoa butter in a candy bar from separating.
There are no studies that show soy-derived lecithin has significant effects on cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood. Unfermented soy products are reported by FDA scientists to interfere with pancreatic enzymes trypsin and chymotripsin. Commercial lecithin, as used by food manufacturers, is a mixture of phospholipids in oil. The lecithin is obtained by  degumming the extracted oil of the seeds. The lecithin is a mixture of various phospholipids, and the composition depends on the origin of the lecithin. A major source of lecithin is soybean oil. Because of the EU-requirement to declare additions of allergens in foods, in addition to regulations regarding Genetically Modified Crops, a gradual shift to other sources of lecithin, e.g., sunflower oil, is taking place.
degumming the extracted oil of the seeds. The lecithin is a mixture of various phospholipids, and the composition depends on the origin of the lecithin. A major source of lecithin is soybean oil. Because of the EU-requirement to declare additions of allergens in foods, in addition to regulations regarding Genetically Modified Crops, a gradual shift to other sources of lecithin, e.g., sunflower oil, is taking place.
The main phospholipids in lecithin from soya and sunflower are phosphatidyl choline, phosphatidyl inositol, phosphatidyl ethanolamine, and phosphatidic acid. They are often abbreviated to PC, PI, PE, and PA, respectively. To modify the performance of lecithin, i.e., to make it suitable for the product to which it is added, it may be hydrolysed enzymatically. In hydrolysed lecithins, a portion of the phospholipids have one fatty acid removed by phospholipase. Such phospholipids are called  lyso-phospholipids. The most commonly-used phospholipase is phospholipase A2, which removes the fatty acid at the sn-2 position.
lyso-phospholipids. The most commonly-used phospholipase is phospholipase A2, which removes the fatty acid at the sn-2 position.
In margarines, especially those containing high levels of fat (>75%), lecithin is added as an 'anti-spattering' agent for shallow frying. Lecithin is admitted by the EU as a food additive, designated by E number E322.
Lecithins may also be modified by a process called fractionation. During this process, lecithin is mixed with an alcohol, usually ethanol. Some phospholipids have a good solubility in ethanol (e.g., phosphatidylcholine), whereas most other phospholipids do not dissolve well in ethanol. The ethanol is separated from the lecithin sludge, after which the ethanol is removed by evaporation, to obtain a phosphatidylcholine-enriched lecithin fraction.
[ edit]Compatibility with special diets
edit]Compatibility with special diets
Thus far, the only proven benefit and suggested use is for those taking niacin to treat high cholesterol. Niacin treatment can deplete choline, necessitating an increased amount of lecithin or choline in the diet.
Egg-derived lecithin may be a concern for those following some specialized diets. Egg lecithin is not a concern for those on low-cholesterol diets, but, if not purified before being used as a food ingredient, it could significantly raise the overall cholesterol content of the food.
For observant Jews under Kashrut, it is considered pareve, neutral, e.g., may be mixed with both meat and dairy. However soy derived lecithin would not be considered kosher for passover as it is kitniyot. For observant Muslims, under Sharia, lecithin from plants, egg yolks or Halal animals is allowed, otherwise it is prohibited. There is no general agreement among vegetarians concerning egg-derived lecithin, but, as it is animal-derived, vegans choose not to consume it.
[ edit]See also
edit]See also
[ edit]References
edit]References
[ edit]External links
edit]External links