|
|
Posted on 2012-11-21 17:21 鑫龍 閱讀(258) 評論(0) 編輯 收藏 引用 所屬分類: JULY_程序員編程藝術

程序員編程藝術:第三章續、Top K算法問題的實現
作者:July,zhouzhenren,yansha。
致謝:微軟100題實現組,狂想曲創作組。
時間:2011年05月08日
微博:http://weibo.com/julyweibo 。
出處:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v 。
wiki:http://tctop.wikispaces.com/。
-----------------------------------------------
前奏
在上一篇文章,程序員面試題狂想曲:第三章、尋找最小的k個數中,后來為了論證類似快速排序中partition的方法在最壞情況下,能在O(N)的時間復雜度內找到最小的k個數,而前前后后updated了10余次。所謂功夫不負苦心人,終于得到了一個想要的結果。 簡單總結如下(詳情,請參考原文第三章):
1、RANDOMIZED-SELECT,以序列中隨機選取一個元素作為主元,可達到線性期望時間O(N)的復雜度。
2、SELECT,快速選擇算法,以序列中“五分化中項的中項”,或“中位數的中位數”作為主元(樞紐元),則不容置疑的可保證在最壞情況下亦為O(N)的復雜度。 本章,咱們來闡述尋找最小的k個數的反面,即尋找最大的k個數,但此刻可能就有讀者質疑了,尋找最大的k個數和尋找最小的k個數,原理不是一樣的么? 是的,的確是一樣,但這個尋找最大的k個數的問題的實用范圍更廣,因為它牽扯到了一個Top K算法問題,以及有關搜索引擎,海量數據處理等廣泛的問題,所以本文特意對這個Top K算法問題,進行闡述以及實現(側重實現,因為那樣看起來,會更令人激動人心),算是第三章的續。ok,有任何問題,歡迎隨時不吝指正。謝謝。 說明 關于尋找最小K個數能做到最壞情況下為O(N)的算法及證明,請參考原第三章,尋找最小的k個數,本文的代碼不保證O(N)的平均時間復雜度,只是根據第三章有辦法可以做到而已(如上面總結的,2、SELECT,快速選擇算法,以序列中“五分化中項的中項”,或“中位數的中位數”作為主元或樞紐元的方法,原第三章已經嚴格論證并得到結果)。 第一節、尋找最小的第k個數 在進入尋找最大的k個數的主題之前,先補充下關于尋找最k小的數的三種簡單實現。由于堆的完整實現,第三章:第五節,堆結構實現,處理海量數據中已經給出,下面主要給出類似快速排序中partition過程的代碼實現: 尋找最小的k個數,實現一(下段代碼經本文評論下多位讀者指出有問題:當a [ i ]=a [ j ]=pivot時,則會產生一個無限循環,在Mark Allen Weiss的數據結構與算法分析C++描述中文版的P209-P210有描述,讀者可參看之。特此說明,因本文代碼存在問題的地方還有幾處,故請待后續統一修正.2012.08.21): - //copyright@ mark allen weiss && July && yansha
- //July,yansha、updated,2011.05.08.
-
- //本程序,后經飛羽找出錯誤,已經修正。
- //隨機選取樞紐元,尋找最小的第k個數
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- using namespace std;
-
- int my_rand(int low, int high)
- {
- int size = high - low + 1;
- return low + rand() % size;
- }
-
- //q_select places the kth smallest element in a[k]
- int q_select(int a[], int k, int left, int right)
- {
- if(k>right)
- {
- cout<<"---------"<<endl; //為了處理當k大于數組中元素個數的異常情況
- return false;
- }
-
- //真正的三數中值作為樞紐元方法,關鍵代碼就是下述六行
- int midIndex = (left + right) / 2;
- if(a[left] < a[midIndex])
- swap(a[left], a[midIndex]);
- if(a[right] < a[midIndex])
- swap(a[right], a[midIndex]);
- if(a[right] < a[left])
- swap(a[right], a[left]);
- swap(a[midIndex], a[right]);
-
- int pivot = a[right]; //之前是int pivot = right,特此,修正。
-
- // 申請兩個移動指針并初始化
- int i = left;
- int j = right-1;
-
- // 根據樞紐元素的值對數組進行一次劃分
- for (;;)
- {
- while(a[i] < pivot)
- i++;
- while(a[j] > pivot)
- j--;
- if (i < j)
- swap(a[i], a[j]);
- else
- break;
- }
- swap(a[i], a[right]);
-
- /* 對三種情況進行處理:(m = i - left + 1)
- 1、如果m=k,即返回的主元即為我們要找的第k小的元素,那么直接返回主元a[i]即可;
- 2、如果m>k,那么接下來要到低區間A[0....m-1]中尋找,丟掉高區間;
- 3、如果m<k,那么接下來要到高區間A[m+1...n-1]中尋找,丟掉低區間。
- */
- int m = i - left + 1;
- if (m == k)
- {
- cout<<a[i]<<endl;
- for(i-=1;i>=0;i--)
- cout<<a[i]<<endl;
- }
- else if(m > k)
- return q_select(a, k, left, i - 1);
- else
- return q_select(a, k - m, i + 1, right);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- int i;
- int a[] = {7, 8, 9, 54, 6, 4, 11, 1, 2, 33};
- q_select(a, 4, 0, sizeof(a) / sizeof(int) - 1);
- return 0;
- }
- //copyright@ July
- //yansha、updated,2011.05.08。
- // 數組中尋找第k小元素,實現二
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
-
- const int numOfArray = 10;
-
- // 這里并非真正隨機
- int my_rand(int low, int high)
- {
- int size = high - low + 1;
- return low + rand() % size;
- }
-
- // 以最末元素作為主元對數組進行一次劃分
- int partition(int array[], int left, int right)
- {
- int pos = right;
- for(int index = right - 1; index >= left; index--)
- {
- if(array[index] > array[right])
- swap(array[--pos], array[index]);
- }
- swap(array[pos], array[right]);
- return pos;
- }
-
- // 隨機快排的partition過程
- int random_partition(int array[], int left, int right)
- {
- // 隨機從范圍left到right中取一個值作為主元
- int index = my_rand(left, right);
- swap(array[right], array[index]);
-
- // 對數組進行劃分,并返回主元在數組中的位置
- return partition(array, left, right);
- }
-
- // 以線性時間返回數組array[left...right]中第k小的元素
- int random_select(int array[], int left, int right, int k)
- {
- // 處理異常情況
- if (k < 1 || k > (right - left + 1))
- return -1;
-
- // 主元在數組中的位置
- int pos = random_partition(array, left, right);
-
- /* 對三種情況進行處理:(m = i - left + 1)
- 1、如果m=k,即返回的主元即為我們要找的第k小的元素,那么直接返回主元array[i]即可;
- 2、如果m>k,那么接下來要到低區間array[left....pos-1]中尋找,丟掉高區間;
- 3、如果m<k,那么接下來要到高區間array[pos+1...right]中尋找,丟掉低區間。
- */
- int m = pos - left + 1;
- if(m == k)
- return array[pos];
- else if (m > k)
- return random_select(array, left, pos - 1, k);
- else
- return random_select(array, pos + 1, right, k - m);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- int array[numOfArray] = {7, 8, 9, 54, 6, 4, 2, 1, 12, 33};
- cout << random_select(array, 0, numOfArray - 1, 4) << endl;
- return 0;
- }
尋找最小的第k個數,實現三: - //求取無序數組中第K個數,本程序樞紐元的選取有問題,不作推薦。
- //copyright@ 飛羽
- //July、yansha,updated,2011.05.18。
- #include <iostream>
- #include <time.h>
- using namespace std;
-
- int kth_elem(int a[], int low, int high, int k)
- {
- int pivot = a[low];
- //這個程序之所以做不到O(N)的最最重要的原因,就在于這個樞紐元的選取。
- //而這個程序直接選取數組中第一個元素作為樞紐元,是做不到平均時間復雜度為 O(N)的。
-
- //要 做到,就必須 把上面選取樞紐元的 代碼改掉,要么是隨機選擇數組中某一元素作為樞紐元,能達到線性期望的時間
- //要么是選取數組中中位數的中位數作為樞紐元,保證最壞情況下,依然為線性O(N)的平均時間復雜度。
- int low_temp = low;
- int high_temp = high;
- while(low < high)
- {
- while(low < high && a[high] >= pivot)
- --high;
- a[low] = a[high];
- while(low < high && a[low] < pivot)
- ++low;
- a[high] = a[low];
- }
- a[low] = pivot;
-
- //以下就是主要思想中所述的內容
- if(low == k - 1)
- return a[low];
- else if(low > k - 1)
- return kth_elem(a, low_temp, low - 1, k);
- else
- return kth_elem(a, low + 1, high_temp, k);
- }
-
- int main() //以后盡量不再用隨機產生的數組進行測試,沒多大必要。
- {
- for (int num = 5000; num < 50000001; num *= 10)
- {
- int *array = new int[num];
-
- int j = num / 10;
- int acc = 0;
- for (int k = 1; k <= num; k += j)
- {
- // 隨機生成數據
- srand(unsigned(time(0)));
- for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
- array[i] = rand() * RAND_MAX + rand();
- //”如果數組本身就是利用隨機化產生的話,那么選擇其中任何一個元素作為樞軸都可以看作等價于隨機選擇樞軸,
- //(雖然這不叫隨機選擇樞紐)”,這句話,是完全不成立的,是錯誤的。
-
- //“因為你總是選擇 隨機數組中第一個元素 作為樞紐元,不是 隨機選擇樞紐元”
- //相當于把上面這句話中前面的 “隨機” 兩字去掉,就是:
- //因為 你總是選擇數組中第一個元素作為樞紐元,不是 隨機選擇樞紐元。
- //所以,這個程序,始終做不到平均時間復雜度為O(N)。
-
- //隨機數組和給定一個非有序而隨機手動輸入的數組,是一個道理。稍后,還將就程序的運行結果繼續解釋這個問題。
- //July、updated,2011.05.18。
-
- // 計算一次查找所需的時鐘周期數
- clock_t start = clock();
- int data = kth_elem(array, 0, num - 1, k);
- clock_t end = clock();
- acc += (end - start);
- }
- cout << "The average time of searching a date in the array size of " << num << " is " << acc / 10 << endl;
- }
- return 0;
- }
The average time of searching a date in the array size of 5000 is 0
The average time of searching a date in the array size of 50000 is 1
The average time of searching a date in the array size of 500000 is 12
The average time of searching a date in the array size of 5000000 is 114
The average time of searching a date in the array size of 50000000 is 1159
Press any key to continue 通過測試這個程序,我們竟發現這個程序的運行時間是線性的?
或許,你還沒有意識到這個問題,ok,聽我慢慢道來。
我們之前說,要保證這個算法是線性的,就一定要在樞紐元的選取上下足功夫:
1、要么是隨機選取樞紐元作為劃分元素
2、要么是取中位數的中位數作為樞紐元劃分元素
現在,這程序直接選取了數組中第一個元素作為樞紐元
竟然,也能做到線性O(N)的復雜度,這不是自相矛盾么?
你覺得這個程序的運行時間是線性O(N),是巧合還是確定會是如此? 哈哈,且看1、@well:根據上面的運行結果不能判斷線性,如果人家是O(n^1.1) 也有可能啊,而且部分數據始終是擬合,還是要數學證明才可靠。2、@July:同時,隨機數組中選取一個元素作為樞紐元!=> 隨機數組中隨機選取一個元素作為樞紐元(如果是隨機選取隨機數組中的一個元素作為主元,那就不同了,跟隨機選取數組中一個元素作為樞紐元一樣了)。3、@飛羽:正是因為數組本身是隨機的,所以選擇第一個元素和隨機選擇其它的數是等價的(由等概率產生保證),這第3點,我與飛羽有分歧,至于誰對誰錯,待時間讓我考證。 關于上面第3點我和飛羽的分歧,在我們進一步討論之后,一致認定(不過,相信,你看到了上面程序更新的注釋之后,你應該有幾分領會了): - 我們說輸入一個數組的元素,不按其順序輸入:如,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,而是這樣輸入:5,7,6,4,3,1,2,這就叫隨機輸入,而這種情況就相當于上述程序主函數中所產生的隨機數組。然而選取隨機輸入的數組或隨機數組中第一個元素作為主元,我們不能稱之為說是隨機選取樞紐元。
- 因為,隨機數產生器產生的數據是隨機的,沒錯,但你要知道,你總是選取隨機數組的第一個元素作為樞紐元,這不叫隨機選取樞紐元。
- 所以,上述程序的主函數中隨機產生的數組對這個程序的算法而言,沒有任何意義,就是幫忙產生了一個隨機數組,幫助我們完成了測試,且方便我們測試大數據量而已,就這么簡單。
- 且一般來說,我們看一個程序的 時間復雜度,是不考慮 其輸入情況的,即不考慮主函數,正如這個 kth number 的程序所見,你每次都是隨機選取數組中第一個元素作為樞紐元,而并不是隨機選擇樞紐元,所以,做不到平均時間復雜度為O(N)。
所以:想要保證此快速選擇算法為O(N)的復雜度,只有兩種途徑,那就是保證劃分的樞紐元元素的選取是:
1、隨機的(注,此樞紐元隨機不等同于數組隨機)
2、五分化中項的中項,或中位數的中位數。 所以,雖然咱們對于一切心知肚明,但上面程序的運行結果說明不了任何問題,這也從側面再次佐證了咱們第三章中觀點的正確無誤性。
updated: 非常感謝飛羽等人的工作,將上述三個版本綜合到了一起(待進一步測試): - ///下面的代碼對July博客中的三個版本代碼進行重新改寫。歡迎指出錯誤。
- ///先把它們貼在這里,還要進行隨機化數據測試。待發...
-
- //modified by 飛羽 at 2011.5.11
- /////Top_K_test
-
- //修改了下命名規范,July、updated,2011.05.12。
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- using namespace std;
-
- inline int my_rand(int low, int high)
- {
- int size = high - low + 1;
- return low + rand() % size;
- }
-
- int partition(int array[], int left, int right)
- {
- int pivot = array[right];
- int pos = left-1;
- for(int index = left; index < right; index++)
- {
- if(array[index] <= pivot)
- swap(array[++pos], array[index]);
- }
- swap(array[++pos], array[right]);
- return pos;//返回pivot所在位置
- }
-
- bool median_select(int array[], int left, int right, int k)
- {
- //第k小元素,實際上應該在數組中下標為k-1
- if (k-1 > right || k-1 < left)
- return false;
-
- //真正的三數中值作為樞紐元方法,關鍵代碼就是下述六行
- int midIndex=(left+right)/2;
- if(array[left]<array[midIndex])
- swap(array[left],array[midIndex]);
- if(array[right]<array[midIndex])
- swap(array[right],array[midIndex]);
- if(array[right]<array[left])
- swap(array[right],array[left]);
- swap(array[midIndex], array[right]);
-
- int pos = partition(array, left, right);
-
- if (pos == k-1)
- return true;
- else if (pos > k-1)
- return median_select(array, left, pos-1, k);
- else return median_select(array, pos+1, right, k);
- }
-
- bool rand_select(int array[], int left, int right, int k)
- {
- //第k小元素,實際上應該在數組中下標為k-1
- if (k-1 > right || k-1 < left)
- return false;
-
- //隨機從數組中選取樞紐元元素
- int Index = my_rand(left, right);
- swap(array[Index], array[right]);
-
- int pos = partition(array, left, right);
-
- if (pos == k-1)
- return true;
- else if (pos > k-1)
- return rand_select(array, left, pos-1, k);
- else return rand_select(array, pos+1, right, k);
- }
-
- bool kth_select(int array[], int left, int right, int k)
- {
- //直接取最原始的劃分操作
- if (k-1 > right || k-1 < left)
- return false;
-
- int pos = partition(array, left, right);
- if(pos == k-1)
- return true;
- else if(pos > k-1)
- return kth_select(array, left, pos-1, k);
- else return kth_select(array, pos+1, right, k);
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- int array1[] = {7, 8, 9, 54, 6, 4, 11, 1, 2, 33};
- int array2[] = {7, 8, 9, 54, 6, 4, 11, 1, 2, 33};
- int array3[] = {7, 8, 9, 54, 6, 4, 11, 1, 2, 33};
-
- int numOfArray = sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int);
- for(int i=0; i<numOfArray; i++)
- printf("%d/t",array1[i]);
-
- int K = 9;
- bool flag1 = median_select(array1, 0, numOfArray-1, K);
- bool flag2 = rand_select(array2, 0, numOfArray-1, K);
- bool flag3 = kth_select(array3, 0, numOfArray-1, K);
- if(!flag1)
- return 1;
- for(i=0; i<K; i++)
- printf("%d/t",array1[i]);
- printf("/n");
-
- if(!flag2)
- return 1;
- for(i=0; i<K; i++)
- printf("%d/t",array2[i]);
- printf("/n");
-
- if(!flag3)
- return 1;
- for(i=0; i<K; i++)
- printf("%d/t",array3[i]);
- printf("/n");
-
- return 0;
- }
說明:@飛羽:因為預先設定了K,經過分割算法后,數組肯定被劃分為array[0...k-1]和array[k...length-1],注意到經過Select_K_Version操作后,數組是被不斷地分割的,使得比array[k-1]的元素小的全在左邊,題目要求的是最小的K個元素,當然也就是array[0...k-1],所以輸出的結果就是前k個最小的數: 7 8 9 54 6 4 11 1 2 33
4 1 2 6 7 8 9 11 33
7 6 4 1 2 8 9 11 33
7 8 9 6 4 11 1 2 33
Press any key to continue (更多,請參見:此狂想曲系列tctop修訂wiki頁面:http://tctop.wikispaces.com/)
第二節、尋找最大的k個數
把之前第三章的問題,改幾個字,即成為尋找最大的k個數的問題了,如下所述:
查找最大的k個元素
題目描述:輸入n個整數,輸出其中最大的k個。
例如輸入1,2,3,4,5,6,7和8這8個數字,則最大的4個數字為8,7,6和5。
分析:由于尋找最大的k個數的問題與之前的尋找最小的k個數的問題,本質是一樣的,所以,這里就簡單闡述下思路,ok,考驗你舉一反三能力的時間到了: 1、排序,快速排序。我們知道,快速排序平均所費時間為n*logn,從小到大排序這n個數,然后再遍歷序列中后k個元素輸出,即可,總的時間復雜度為O(n*logn+k)=O(n*logn)。 2、排序,選擇排序。用選擇或交換排序,即遍歷n個數,先把最先遍歷到得k個數存入大小為k的數組之中,對這k個數,利用選擇或交換排序,找到k個數中的最小數kmin(kmin設為k個元素的數組中最小元素),用時O(k)(你應該知道,插入或選擇排序查找操作需要O(k)的時間),后再繼續遍歷后n-k個數,x與kmin比較:如果x>kmin,則x代替kmin,并再次重新找出k個元素的數組中最大元素kmin‘(多謝jiyeyuran 提醒修正);如果x<kmin,則不更新數組。這樣,每次更新或不更新數組的所用的時間為O(k)或O(0),整趟下來,總的時間復雜度平均下來為:n*O(k)=O(n*k)。 3、維護k個元素的最小堆,原理與上述第2個方案一致,即用容量為k的最小堆存儲最先遍歷到的k個數,并假設它們即是最大的k個數,建堆費時O(k),并調整堆(費時O(logk))后,有k1>k2>...kmin(kmin設為小頂堆中最小元素)。繼續遍歷數列,每次遍歷一個元素x,與堆頂元素比較,若x>kmin,則更新堆(用時logk),否則不更新堆。這樣下來,總費時O(k*logk+(n-k)*logk)=O(n*logk)。此方法得益于在堆中,查找等各項操作時間復雜度均為logk(不然,就如上述思路2所述:直接用數組也可以找出最大的k個元素,用時O(n*k))。 4、按編程之美第141頁上解法二的所述,類似快速排序的劃分方法,N個數存儲在數組S中,再從數組中隨機選取一個數X,把數組劃分為Sa和Sb倆部分,Sa>=X>=Sb,如果要查找的k個元素小于Sa的元素個數,則返回Sa中較大的k個元素,否則返回Sa中所有的元素+Sb中最大的k-|Sa|個元素。不斷遞歸下去,把問題分解成更小的問題,平均時間復雜度為O(N)(編程之美所述的n*logk的復雜度有誤,應為O(N),特此訂正。其嚴格證明,請參考第三章:程序員面試題狂想曲:第三章、尋找最小的k個數、updated 10次)。
.........
其它的方法,在此不再重復了,同時,尋找最小的k個數借助堆的實現,代碼在上一篇文章第三章已有給出,更多,可參考第三章,只要把最大堆改成最小堆,即可。
第三節、Top K 算法問題
3.1、搜索引擎熱門查詢統計
題目描述:
搜索引擎會通過日志文件把用戶每次檢索使用的所有檢索串都記錄下來,每個查詢串的長度為1-255字節。
假設目前有一千萬個記錄(這些查詢串的重復度比較高,雖然總數是1千萬,但如果除去重復后,不超過3百萬個。一個查詢串的重復度越高,說明查詢它的用戶越多,也就是越熱門。),請你統計最熱門的10個查詢串,要求使用的內存不能超過1G。 分析:這個問題在之前的這篇文章十一、從頭到尾徹底解析Hash表算法里,已經有所解答。方法是: 第一步、先對這批海量數據預處理,在O(N)的時間內用Hash表完成統計(之前寫成了排序,特此訂正。July、2011.04.27);
第二步、借助堆這個數據結構,找出Top K,時間復雜度為N‘logK。
即,借助堆結構,我們可以在log量級的時間內查找和調整/移動。因此,維護一個K(該題目中是10)大小的小根堆(K1>K2>....Kmin,Kmin設為堆頂元素),然后遍歷300萬的Query,分別和根元素Kmin進行對比比較(如上第2節思路3所述,若X>Kmin,則更新并調整堆,否則,不更新),我們最終的時間復雜度是:O(N) + N'*O(logK),(N為1000萬,N’為300萬)。ok,更多,詳情,請參考原文。 或者:采用trie樹,關鍵字域存該查詢串出現的次數,沒有出現為0。最后用10個元素的最小推來對出現頻率進行排序。 ok,本章里,咱們來實現這個問題,為了降低實現上的難度,假設這些記錄全部是一些英文單詞,即用戶在搜索框里敲入一個英文單詞,然后查詢搜索結果,最后,要你統計輸入單詞中頻率最大的前K個單詞。ok,復雜問題簡單化了之后,編寫代碼實現也相對輕松多了,畫的簡單示意圖(繪制者,yansha),如下: 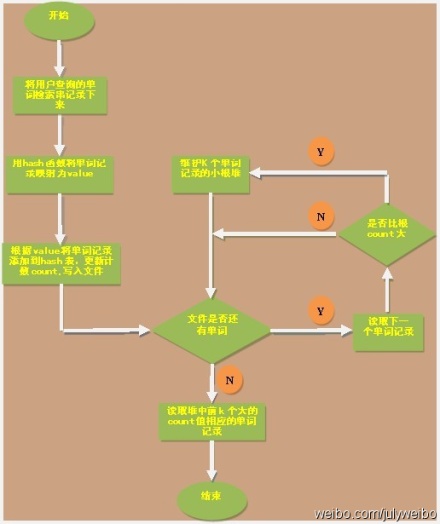
完整源碼: - //copyright@yansha &&July
- //July、updated,2011.05.08
-
- //題目描述:
- //搜索引擎會通過日志文件把用戶每次檢索使用的所有檢索串都記錄下來,每個查詢串的
- //長度為1-255字節。假設目前有一千萬個記錄(這些查詢串的重復度比較高,雖然總數是1千萬,但如果
- //除去重復后,不超過3百萬個。一個查詢串的重復度越高,說明查詢它的用戶越多,也就是越熱門),
- //請你統計最熱門的10個查詢串,要求使用的內存不能超過1G。
-
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <assert.h>
- using namespace std;
-
- #define HASHLEN 2807303
- #define WORDLEN 30
-
- // 結點指針
- typedef struct node_no_space *ptr_no_space;
- typedef struct node_has_space *ptr_has_space;
- ptr_no_space head[HASHLEN];
-
- struct node_no_space
- {
- char *word;
- int count;
- ptr_no_space next;
- };
-
- struct node_has_space
- {
- char word[WORDLEN];
- int count;
- ptr_has_space next;
- };
-
- // 最簡單hash函數
- int hash_function(char const *p)
- {
- int value = 0;
- while (*p != '/0')
- {
- value = value * 31 + *p++;
- if (value > HASHLEN)
- value = value % HASHLEN;
- }
- return value;
- }
-
- // 添加單詞到hash表
- void append_word(char const *str)
- {
- int index = hash_function(str);
- ptr_no_space p = head[index];
- while (p != NULL)
- {
- if (strcmp(str, p->word) == 0)
- {
- (p->count)++;
- return;
- }
- p = p->next;
- }
-
- // 新建一個結點
- ptr_no_space q = new node_no_space;
- q->count = 1;
- q->word = new char [strlen(str)+1];
- strcpy(q->word, str);
- q->next = head[index];
- head[index] = q;
- }
-
-
- // 將單詞處理結果寫入文件
- void write_to_file()
- {
- FILE *fp = fopen("result.txt", "w");
- assert(fp);
-
- int i = 0;
- while (i < HASHLEN)
- {
- for (ptr_no_space p = head[i]; p != NULL; p = p->next)
- fprintf(fp, "%s %d/n", p->word, p->count);
- i++;
- }
- fclose(fp);
- }
-
- // 從上往下篩選,保持小根堆
- void sift_down(node_has_space heap[], int i, int len)
- {
- int min_index = -1;
- int left = 2 * i;
- int right = 2 * i + 1;
-
- if (left <= len && heap[left].count < heap[i].count)
- min_index = left;
- else
- min_index = i;
-
- if (right <= len && heap[right].count < heap[min_index].count)
- min_index = right;
-
- if (min_index != i)
- {
- // 交換結點元素
- swap(heap[i].count, heap[min_index].count);
-
- char buffer[WORDLEN];
- strcpy(buffer, heap[i].word);
- strcpy(heap[i].word, heap[min_index].word);
- strcpy(heap[min_index].word, buffer);
-
- sift_down(heap, min_index, len);
- }
- }
-
- // 建立小根堆
- void build_min_heap(node_has_space heap[], int len)
- {
- if (heap == NULL)
- return;
-
- int index = len / 2;
- for (int i = index; i >= 1; i--)
- sift_down(heap, i, len);
- }
-
- // 去除字符串前后符號
- void handle_symbol(char *str, int n)
- {
- while (str[n] < '0' || (str[n] > '9' && str[n] < 'A') || (str[n] > 'Z' && str[n] < 'a') || str[n] > 'z')
- {
- str[n] = '/0';
- n--;
- }
-
- while (str[0] < '0' || (str[0] > '9' && str[0] < 'A') || (str[0] > 'Z' && str[0] < 'a') || str[0] > 'z')
- {
- int i = 0;
- while (i < n)
- {
- str[i] = str[i+1];
- i++;
- }
- str[i] = '/0';
- n--;
- }
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- char str[WORDLEN];
- for (int i = 0; i < HASHLEN; i++)
- head[i] = NULL;
-
- // 將字符串用hash函數轉換成一個整數并統計出現頻率
- FILE *fp_passage = fopen("string.txt", "r");
- assert(fp_passage);
- while (fscanf(fp_passage, "%s", str) != EOF)
- {
- int n = strlen(str) - 1;
- if (n > 0)
- handle_symbol(str, n);
- append_word(str);
- }
- fclose(fp_passage);
-
- // 將統計結果輸入文件
- write_to_file();
-
- int n = 10;
- ptr_has_space heap = new node_has_space [n+1];
-
- int c;
-
- FILE *fp_word = fopen("result.txt", "r");
- assert(fp_word);
- for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
- {
- fscanf(fp_word, "%s %d", &str, &c);
- heap[j].count = c;
- strcpy(heap[j].word, str);
- }
-
- // 建立小根堆
- build_min_heap(heap, n);
-
- // 查找出現頻率最大的10個單詞
- while (fscanf(fp_word, "%s %d", &str, &c) != EOF)
- {
- if (c > heap[1].count)
- {
- heap[1].count = c;
- strcpy(heap[1].word, str);
- sift_down(heap, 1, n);
- }
- }
- fclose(fp_word);
-
- // 輸出出現頻率最大的單詞
- for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
- cout << heap[k].count << " " << heap[k].word << endl;
-
- return 0;
- }
程序測試:咱們接下來,來對下面的通過用戶輸入單詞后,搜索引擎記錄下來,“大量”單詞記錄進行統計(同時,令K=10,即要你找出10個最熱門查詢的單詞): 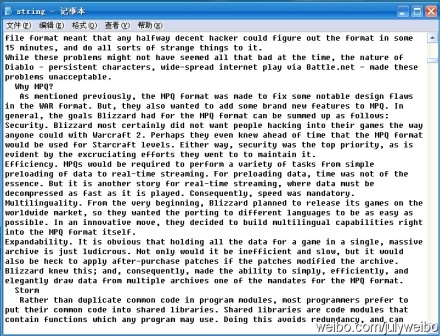
運行結果:根據程序的運行結果,可以看到,搜索引擎記錄下來的查詢次數最多的10個單詞為(注,并未要求這10個數要有序輸出):in(312次),it(384次),a(432),that(456),MPQ(408),of(504),and(624),is(456),the(1008),to(936)。 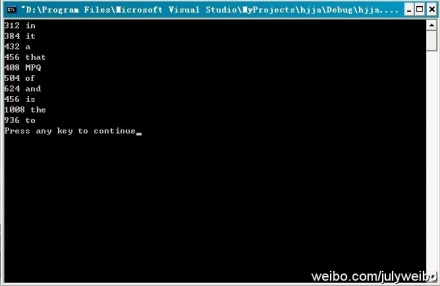
讀者反饋from 楊忠勝:3.1節的代碼第38行 hash_function(char const *p)有誤吧,這樣的話,不能修改p的值(但是函數需要修改指針的值),要想不修改*p指向的內容,應該是const char *p; 此外,您程序中的/t, /n有誤,C語言是\t,\n。
感謝這位讀者的來信,日后統一訂正。謝謝。 3.2、統計出現次數最多的數據 題目描述:
給你上千萬或上億數據(有重復),統計其中出現次數最多的前N個數據。 分析:上千萬或上億的數據,現在的機器的內存應該能存下(也許可以,也許不可以)。所以考慮采用hash_map/搜索二叉樹/紅黑樹等來進行統計次數。然后就是取出前N個出現次數最多的數據了。當然,也可以堆實現。 ok,此題與上題類似,最好的方法是用hash_map統計出現的次數,然后再借用堆找出出現次數最多的N個數據。不過,上一題統計搜索引擎最熱門的查詢已經采用過hash表統計單詞出現的次數,特此,本題咱們改用紅黑樹取代之前的用hash表,來完成最初的統計,然后用堆更新,找出出現次數最多的前N個數據。 同時,正好個人此前用c && c++ 語言實現過紅黑樹,那么,代碼能借用就借用吧。
完整代碼: - //copyright@ zhouzhenren &&July
- //July、updated,2011.05.08.
-
- //題目描述:
- //上千萬或上億數據(有重復),統計其中出現次數最多的前N個數據
-
- //解決方案:
- //1、采用紅黑樹(本程序中有關紅黑樹的實現代碼來源于@July)來進行統計次數。
- //2、然后遍歷整棵樹,同時采用最小堆更新前N個出現次數最多的數據。
-
- //聲明:版權所有,引用必須注明出處。
- #define PARENT(i) (i)/2
- #define LEFT(i) 2*(i)
- #define RIGHT(i) 2*(i)+1
-
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
-
- typedef enum rb_color{ RED, BLACK }RB_COLOR;
- typedef struct rb_node
- {
- int key;
- int data;
- RB_COLOR color;
- struct rb_node* left;
- struct rb_node* right;
- struct rb_node* parent;
- }RB_NODE;
-
- RB_NODE* RB_CreatNode(int key, int data)
- {
- RB_NODE* node = (RB_NODE*)malloc(sizeof(RB_NODE));
- if (NULL == node)
- {
- printf("malloc error!");
- exit(-1);
- }
-
- node->key = key;
- node->data = data;
- node->color = RED;
- node->left = NULL;
- node->right = NULL;
- node->parent = NULL;
-
- return node;
- }
-
- /**
- * 左旋
- *
- * node right
- * / / ==> / /
- * a right node y
- * / / / /
- * b y a b
- */
- RB_NODE* RB_RotateLeft(RB_NODE* node, RB_NODE* root)
- {
- RB_NODE* right = node->right; // 指定指針指向 right<--node->right
-
- if ((node->right = right->left))
- right->left->parent = node; // 好比上面的注釋圖,node成為b的父母
-
- right->left = node; // node成為right的左孩子
-
- if ((right->parent = node->parent))
- {
- if (node == node->parent->right)
- node->parent->right = right;
- else
- node->parent->left = right;
- }
- else
- root = right;
-
- node->parent = right; //right成為node的父母
-
- return root;
- }
-
- /**
- * 右旋
- *
- * node left
- * / / / /
- * left y ==> a node
- * / / / /
- * a b b y
- */
- RB_NODE* RB_RotateRight(RB_NODE* node, RB_NODE* root)
- {
- RB_NODE* left = node->left;
-
- if ((node->left = left->right))
- left->right->parent = node;
-
- left->right = node;
-
- if ((left->parent = node->parent))
- {
- if (node == node->parent->right)
- node->parent->right = left;
- else
- node->parent->left = left;
- }
- else
- root = left;
-
- node->parent = left;
-
- return root;
- }
-
- /**
- * 紅黑樹的3種插入情況
- * 用z表示當前結點, p[z]表示父母、p[p[z]]表示祖父, y表示叔叔.
- */
- RB_NODE* RB_Insert_Rebalance(RB_NODE* node, RB_NODE* root)
- {
- RB_NODE *parent, *gparent, *uncle, *tmp; //父母p[z]、祖父p[p[z]]、叔叔y、臨時結點*tmp
-
- while ((parent = node->parent) && parent->color == RED)
- { // parent 為node的父母,且當父母的顏色為紅時
- gparent = parent->parent; // gparent為祖父
-
- if (parent == gparent->left) // 當祖父的左孩子即為父母時,其實上述幾行語句,無非就是理順孩子、父母、祖父的關系。
- {
- uncle = gparent->right; // 定義叔叔的概念,叔叔y就是父母的右孩子。
- if (uncle && uncle->color == RED) // 情況1:z的叔叔y是紅色的
- {
- uncle->color = BLACK; // 將叔叔結點y著為黑色
- parent->color = BLACK; // z的父母p[z]也著為黑色。解決z,p[z]都是紅色的問題。
- gparent->color = RED;
- node = gparent; // 將祖父當做新增結點z,指針z上移倆層,且著為紅色。
- // 上述情況1中,只考慮了z作為父母的右孩子的情況。
- }
- else // 情況2:z的叔叔y是黑色的,
- {
- if (parent->right == node) // 且z為右孩子
- {
- root = RB_RotateLeft(parent, root); // 左旋[結點z,與父母結點]
- tmp = parent;
- parent = node;
- node = tmp; // parent與node 互換角色
- }
- // 情況3:z的叔叔y是黑色的,此時z成為了左孩子。
- // 注意,1:情況3是由上述情況2變化而來的。
- // ......2:z的叔叔總是黑色的,否則就是情況1了。
- parent->color = BLACK; // z的父母p[z]著為黑色
- gparent->color = RED; // 原祖父結點著為紅色
- root = RB_RotateRight(gparent, root); // 右旋[結點z,與祖父結點]
- }
- }
-
- else
- {
- // 這部分是特別為情況1中,z作為左孩子情況,而寫的。
- uncle = gparent->left; // 祖父的左孩子作為叔叔結點。[原理還是與上部分一樣的]
- if (uncle && uncle->color == RED) // 情況1:z的叔叔y是紅色的
- {
- uncle->color = BLACK;
- parent->color = BLACK;
- gparent->color = RED;
- node = gparent; // 同上
- }
- else // 情況2:z的叔叔y是黑色的,
- {
- if (parent->left == node) // 且z為左孩子
- {
- root = RB_RotateRight(parent, root); // 以結點parent、root右旋
- tmp = parent;
- parent = node;
- node = tmp; // parent與node 互換角色
- }
- // 經過情況2的變化,成為了情況3.
- parent->color = BLACK;
- gparent->color = RED;
- root = RB_RotateLeft(gparent, root); // 以結點gparent和root左旋
- }
- }
- }
-
- root->color = BLACK; // 根結點,不論怎樣,都得置為黑色。
- return root; // 返回根結點。
- }
-
- /**
- * 紅黑樹查找結點
- * rb_search_auxiliary:查找
- * rb_node_t* rb_search:返回找到的結點
- */
- RB_NODE* RB_SearchAuxiliary(int key, RB_NODE* root, RB_NODE** save)
- {
- RB_NODE* node = root;
- RB_NODE* parent = NULL;
- int ret;
-
- while (node)
- {
- parent = node;
- ret = node->key - key;
- if (0 < ret)
- node = node->left;
- else if (0 > ret)
- node = node->right;
- else
- return node;
- }
-
- if (save)
- *save = parent;
-
- return NULL;
- }
-
- /**
- * 返回上述rb_search_auxiliary查找結果
- */
- RB_NODE* RB_Search(int key, RB_NODE* root)
- {
- return RB_SearchAuxiliary(key, root, NULL);
- }
-
- /**
- * 紅黑樹的插入
- */
- RB_NODE* RB_Insert(int key, int data, RB_NODE* root)
- {
- RB_NODE* parent = NULL;
- RB_NODE* node = NULL;
-
- parent = NULL;
- if ((node = RB_SearchAuxiliary(key, root, &parent))) // 調用RB_SearchAuxiliary找到插入結點的地方
- {
- node->data++; // 節點已經存在data值加1
- return root;
- }
-
- node = RB_CreatNode(key, data); // 分配結點
- node->parent = parent;
-
- if (parent)
- {
- if (parent->key > key)
- parent->left = node;
- else
- parent->right = node;
- }
- else
- {
- root = node;
- }
-
- return RB_Insert_Rebalance(node, root); // 插入結點后,調用RB_Insert_Rebalance修復紅黑樹的性質
- }
-
- typedef struct rb_heap
- {
- int key;
- int data;
- }RB_HEAP;
- const int heapSize = 10;
- RB_HEAP heap[heapSize+1];
-
- /**
- * MAX_HEAPIFY函數對堆進行更新,使以i為根的子樹成最大堆
- */
- void MIN_HEAPIFY(RB_HEAP* A, const int& size, int i)
- {
- int l = LEFT(i);
- int r = RIGHT(i);
- int smallest = i;
-
- if (l <= size && A[l].data < A[i].data)
- smallest = l;
- if (r <= size && A[r].data < A[smallest].data)
- smallest = r;
-
- if (smallest != i)
- {
- RB_HEAP tmp = A[i];
- A[i] = A[smallest];
- A[smallest] = tmp;
- MIN_HEAPIFY(A, size, smallest);
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * BUILD_MINHEAP函數對數組A中的數據建立最小堆
- */
- void BUILD_MINHEAP(RB_HEAP* A, const int& size)
- {
- for (int i = size/2; i >= 1; --i)
- MIN_HEAPIFY(A, size, i);
- }
-
-
- /*
- 3、維護k個元素的最小堆,原理與上述第2個方案一致,
- 即用容量為k的最小堆存儲最先在紅黑樹中遍歷到的k個數,并假設它們即是最大的k個數,建堆費時O(k),
- 然后調整堆(費時O(logk))后,有k1>k2>...kmin(kmin設為小頂堆中最小元素)。
- 繼續中序遍歷紅黑樹,每次遍歷一個元素x,與堆頂元素比較,若x>kmin,則更新堆(用時logk),否則不更新堆。
- 這樣下來,總費時O(k*logk+(n-k)*logk)=O(n*logk)。
- 此方法得益于在堆中,查找等各項操作時間復雜度均為logk)。
- */
-
- //中序遍歷RBTree
- void InOrderTraverse(RB_NODE* node)
- {
- if (node == NULL)
- {
- return;
- }
- else
- {
- InOrderTraverse(node->left);
- if (node->data > heap[1].data) // 當前節點data大于最小堆的最小元素時,更新堆數據
- {
- heap[1].data = node->data;
- heap[1].key = node->key;
- MIN_HEAPIFY(heap, heapSize, 1);
- }
- InOrderTraverse(node->right);
- }
- }
-
- void RB_Destroy(RB_NODE* node)
- {
- if (NULL == node)
- {
- return;
- }
- else
- {
- RB_Destroy(node->left);
- RB_Destroy(node->right);
- free(node);
- node = NULL;
- }
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- RB_NODE* root = NULL;
- RB_NODE* node = NULL;
-
- // 初始化最小堆
- for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)
- {
- heap[i].key = i;
- heap[i].data = -i;
- }
- BUILD_MINHEAP(heap, heapSize);
-
- FILE* fp = fopen("data.txt", "r");
- int num;
- while (!feof(fp))
- {
- fscanf(fp, "%d", &num);
- root = RB_Insert(num, 1, root);
- }
- fclose(fp);
-
- InOrderTraverse(root); //遞歸遍歷紅黑樹
- RB_Destroy(root);
-
- for (i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)
- {
- printf("%d/t%d/n", heap[i].key, heap[i].data);
- }
- return 0;
- }
程序測試:咱們來對下面這個小文件進行測試: 
運行結果:如下圖所示, 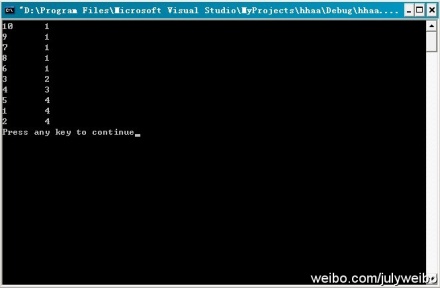
問題補遺: ok,由于在遍歷紅黑樹采用的是遞歸方式比較耗內存,下面給出一個非遞歸遍歷的程序(下述代碼若要運行,需貼到上述程序之后,因為其它的代碼未變,只是在遍歷紅黑樹的時候,采取非遞歸遍歷而已,同時,主函數的編寫也要稍微修改下): - //copyright@ zhouzhenren
- //July、updated,2011.05.08.
- #define STACK_SIZE 1000
- typedef struct
- { // 棧的結點定義
- RB_NODE** top;
- RB_NODE** base;
- }*PStack, Stack;
-
- bool InitStack(PStack& st) // 初始化棧
- {
- st->base = (RB_NODE**)malloc(sizeof(RB_NODE*) * STACK_SIZE);
- if (!st->base)
- {
- printf("InitStack error!");
- exit(1);
- }
- st->top = st->base;
- return true;
- }
-
- bool Push(PStack& st, RB_NODE*& e) // 入棧
- {
- if (st->top - st->base >= STACK_SIZE)
- return false;
- *st->top = e;
- st->top++;
- return true;
- }
-
- bool Pop(PStack& st, RB_NODE*& e) // 出棧
- {
- if (st->top == st->base)
- {
- e = NULL;
- return false;
- }
- e = *--st->top;
- return true;
- }
-
- bool StackEmpty(PStack& st) // 棧是否為空
- {
- if (st->base == st->top)
- return true;
- else
- return false;
- }
-
- bool InOrderTraverse_Stack(RB_NODE*& T) // 中序遍歷
- {
- PStack S = (PStack)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
- RB_NODE* P = T;
- InitStack(S);
- while (P != NULL || !StackEmpty(S))
- {
- if (P != NULL)
- {
- Push(S, P);
- P = P->left;
- }
- else
- {
- Pop(S, P);
- if (P->data > heap[1].data) // 當前節點data大于最小堆的最小元素時,更新堆數據
- {
- heap[1].data = P->data;
- heap[1].key = P->key;
- MIN_HEAPIFY(heap, heapSize, 1);
- }
- P = P->right;
- }
- }
- free(S->base);
- S->base = NULL;
- free(S);
- S = NULL;
-
- return true;
- }
-
- bool PostOrderTraverse_Stack(RB_NODE*& T) //后序遍歷
- {
- PStack S = (PStack)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
- RB_NODE* P = T;
- RB_NODE* Pre = NULL;
- InitStack(S);
- while (P != NULL || !StackEmpty(S))
- {
- if (P != NULL) // 非空直接入棧
- {
- Push(S, P);
- P = P->left;
- }
- else
- {
- Pop(S, P); // 彈出棧頂元素賦值給P
- if (P->right == NULL || P->right == Pre) // P的右子樹空或是右子樹是剛訪問過的
- { // 節點,則釋放當前節點內存
- free(P);
- Pre = P;
- P = NULL;
- }
- else // 反之,當前節點重新入棧,接著判斷右子樹
- {
- Push(S, P);
- P = P->right;
- }
- }
- }
- free(S->base);
- S->base = NULL;
- free(S);
- S = NULL;
-
- return true;
- }
-
- //主函數稍微修改如下:
- int main()
- {
- RB_NODE* root = NULL;
- RB_NODE* node = NULL;
-
- // 初始化最小堆
- for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)
- {
- heap[i].key = i;
- heap[i].data = -i;
- }
- BUILD_MINHEAP(heap, heapSize);
-
- FILE* fp = fopen("data.txt", "r");
- int num;
- while (!feof(fp))
- {
- fscanf(fp, "%d", &num);
- root = RB_Insert(num, 1, root);
- }
- fclose(fp);
-
- //若上面的程序后面加上了上述的非遞歸遍歷紅黑樹的代碼,那么以下幾行代碼,就得修改如下:
- //InOrderTraverse(root); //此句去掉(遞歸遍歷樹)
- InOrderTraverse_Stack(root); // 非遞歸遍歷樹
-
- //RB_Destroy(root); //此句去掉(通過遞歸釋放內存)
- PostOrderTraverse_Stack(root); // 非遞歸釋放內存
-
- for (i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)
- {
- printf("%d/t%d/n", heap[i].key, heap[i].data);
- }
- return 0;
- }
updated: 后來,我們狂想曲創作組中的3又用hash+堆實現了上題,很明顯比采用上面的紅黑樹,整個實現簡潔了不少,其完整源碼如下: 完整源碼:
- //Author: zhouzhenren
- //Description: 上千萬或上億數據(有重復),統計其中出現次數最多的錢N個數據
-
- //Algorithm: 采用hash_map來進行統計次數+堆(找出Top K)。
- //July,2011.05.12。紀念汶川地震三周年,默哀三秒。
-
- #define PARENT(i) (i)/2
- #define LEFT(i) 2*(i)
- #define RIGHT(i) 2*(i)+1
-
- #define HASHTABLESIZE 2807303
- #define HEAPSIZE 10
- #define A 0.6180339887
- #define M 16384 //m=2^14
-
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- typedef struct hash_node
- {
- int data;
- int count;
- struct hash_node* next;
- }HASH_NODE;
- HASH_NODE* hash_table[HASHTABLESIZE];
-
- HASH_NODE* creat_node(int& data)
- {
- HASH_NODE* node = (HASH_NODE*)malloc(sizeof(HASH_NODE));
-
- if (NULL == node)
- {
- printf("malloc node failed!/n");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
-
- node->data = data;
- node->count = 1;
- node->next = NULL;
- return node;
- }
-
- /**
- * hash函數采用乘法散列法
- * h(k)=int(m*(A*k mod 1))
- */
- int hash_function(int& key)
- {
- double result = A * key;
- return (int)(M * (result - (int)result));
- }
-
- void insert(int& data)
- {
- int index = hash_function(data);
- HASH_NODE* pnode = hash_table[index];
- while (NULL != pnode)
- { // 以存在data,則count++
- if (pnode->data == data)
- {
- pnode->count += 1;
- return;
- }
- pnode = pnode->next;
- }
-
- // 建立一個新的節點,在表頭插入
- pnode = creat_node(data);
- pnode->next = hash_table[index];
- hash_table[index] = pnode;
- }
-
- /**
- * destroy_node釋放創建節點產生的所有內存
- */
- void destroy_node()
- {
- HASH_NODE* p = NULL;
- HASH_NODE* tmp = NULL;
- for (int i = 0; i < HASHTABLESIZE; ++i)
- {
- p = hash_table[i];
- while (NULL != p)
- {
- tmp = p;
- p = p->next;
- free(tmp);
- tmp = NULL;
- }
- }
- }
-
- typedef struct min_heap
- {
- int count;
- int data;
- }MIN_HEAP;
- MIN_HEAP heap[HEAPSIZE + 1];
-
- /**
- * min_heapify函數對堆進行更新,使以i為跟的子樹成最大堆
- */
- void min_heapify(MIN_HEAP* H, const int& size, int i)
- {
- int l = LEFT(i);
- int r = RIGHT(i);
- int smallest = i;
-
- if (l <= size && H[l].count < H[i].count)
- smallest = l;
- if (r <= size && H[r].count < H[smallest].count)
- smallest = r;
-
- if (smallest != i)
- {
- MIN_HEAP tmp = H[i];
- H[i] = H[smallest];
- H[smallest] = tmp;
- min_heapify(H, size, smallest);
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * build_min_heap函數對數組A中的數據建立最小堆
- */
- void build_min_heap(MIN_HEAP* H, const int& size)
- {
- for (int i = size/2; i >= 1; --i)
- min_heapify(H, size, i);
- }
-
- /**
- * traverse_hashtale函數遍歷整個hashtable,更新最小堆
- */
- void traverse_hashtale()
- {
- HASH_NODE* p = NULL;
- for (int i = 0; i < HASHTABLESIZE; ++i)
- {
- p = hash_table[i];
- while (NULL != p)
- { // 如果當前節點的數量大于最小堆的最小值,則更新堆
- if (p->count > heap[1].count)
- {
- heap[1].count = p->count;
- heap[1].data = p->data;
- min_heapify(heap, HEAPSIZE, 1);
- }
- p = p->next;
- }
- }
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- // 初始化最小堆
- for (int i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)
- {
- heap[i].count = -i;
- heap[i].data = i;
- }
- build_min_heap(heap, HEAPSIZE);
-
- FILE* fp = fopen("data.txt", "r");
- int num;
- while (!feof(fp))
- {
- fscanf(fp, "%d", &num);
- insert(num);
- }
- fclose(fp);
-
- traverse_hashtale();
-
- for (i = 1; i <= 10; ++i)
- {
- printf("%d/t%d/n", heap[i].data, heap[i].count);
- }
-
- return 0;
- }
程序測試:對65047kb的數據量文件,進行測試統計(不過,因其數據量實在太大,半天沒打開): 
運行結果:如下, 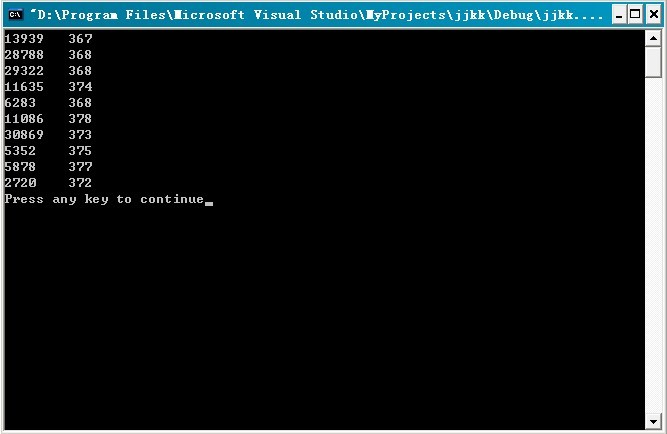
第四節、海量數據處理問題一般總結 關于海量數據處理的問題,一般有Bloom filter,Hashing,bit-map,堆,trie樹等方法來處理。更詳細的介紹,請查看此文:十道海量數據處理面試題與十個方法大總結。 余音 反饋:此文發布后,走進搜索引擎的作者&&深入搜索引擎-海量信息的壓縮、索引和查詢的譯者,梁斌老師,對此文提了點意見,如下:1、首先TopK問題,肯定需要有并發的,否則串行搞肯定慢,IO和計算重疊度不高。其次在IO上需要一些技巧,當然可能只是驗證算法,在實踐中IO的提升會非常明顯。最后上文的代碼可讀性雖好,但機器的感覺可能就會差,這樣會影響性能。2、同時,TopK可以看成從地球上選拔k個跑的最快的,參加奧林匹克比賽,各個國家自行選拔,各個大洲選拔,層層選拔,最后找出最快的10個。發揮多機多核的優勢。 預告:程序員面試題狂想曲、第四章,本月月底之前發布(盡最大努力)。 修訂 程序員面試題狂想曲-tctop(the crazy thingking of programers)的修訂wiki(http://tctop.wikispaces.com/)已于今天建立,我們急切的想得到讀者的反饋,意見,建議,以及更好的思路,算法,和代碼優化的建議。所以, - 如果你發現了狂想曲系列中的任何一題,任何一章(http://t.cn/hgVPmH)中的錯誤,問題,與漏洞,歡迎告知給我們,我們將感激不盡,同時,免費贈送本blog內的全部博文集錦的CHM文件1期;
- 如果你能對狂想曲系列的創作提供任何建設性意見,或指導,歡迎反饋給我們,并真誠邀請您加入到狂想曲的wiki修訂工作中;
- 如果你是編程高手,對狂想曲的任何一章有自己更好的思路,或算法,歡迎加入狂想曲的創作組,以為千千萬萬的讀者創造更多的價值,更好的服務。
Ps:狂想曲tctop的wiki修訂地址為:http://tctop.wikispaces.com/。歡迎圍觀,更歡迎您加入到狂想曲的創作或wiki修訂中。
聯系July
•email,zhoulei0907@yahoo.cn
•blog,http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v 。
•weibo,http://weibo.com/julyweibo 。 作者按:有任何問題,或建議,歡迎以上述聯系方式call me,真誠的謝謝各位。
July、狂想曲創作組,二零一一年五月十日。
版權所有,本人對本blog內所有任何內容享有版權及著作權。實要轉載,請以鏈接形式注明出處。
|