最少攔截系統
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 5453 Accepted Submission(s): 2077
Problem Description
某國為了防御敵國的導彈襲擊,發展出一種導彈攔截系統.但是這種導彈攔截系統有一個缺陷:雖然它的第一發炮彈能夠到達任意的高度,但是以后每一發炮彈都不能超過前一發的高度.某天,雷達捕捉到敵國的導彈來襲.由于該系統還在試用階段,所以只有一套系統,因此有可能不能攔截所有的導彈.
怎么辦呢?多搞幾套系統唄!你說說倒蠻容易,成本呢?成本是個大問題啊.所以俺就到這里來求救了,請幫助計算一下最少需要多少套攔截系統.
Input
輸入若干組數據.每組數據包括:導彈總個數(正整數),導彈依此飛來的高度(雷達給出的高度數據是不大于30000的正整數,用空格分隔)
Output
對應每組數據輸出攔截所有導彈最少要配備多少套這種導彈攔截系統.
Sample Input
8 389 207 155 300 299 170 158 65
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
JGShining
/*
HDU 1257
為了使得使用的攔截系統最少,自然是要考慮使用與當前高度最接近的系統攔截(應該是貪心算法)
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#define INF 0x7ffffff
#define MAXN 10000
int dp[MAXN];//dp[i]代表第i個導彈當前攔截的高度
int main()
{
int n,x,i,res,flag;
int minh;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
res=0;
while(n--)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
flag=0;
minh=INF;
for(i=0;i<res;i++)
{
if(x<=dp[i]&&minh>dp[i]-x)
{
minh=dp[i]-x;
dp[i]=x;
flag=1;
}
}
if(flag==0)
{
dp[res]=x;
res++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",res);
}
return 0;
}
I NEED A OFFER!
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 6119 Accepted Submission(s): 2129
Problem Description
Speakless很早就想出國,現在他已經考完了所有需要的考試,準備了所有要準備的材料,于是,便需要去申請學校了。要申請國外的任何大學,你都要交納一定的申請費用,這可是很驚人的。Speakless沒有多少錢,總共只攢了n萬美元。他將在m個學校中選擇若干的(當然要在他的經濟承受范圍內)。每個學校都有不同的申請費用a(萬美元),并且Speakless估計了他得到這個學校offer的可能性b。不同學校之間是否得到offer不會互相影響。“I NEED A OFFER”,他大叫一聲。幫幫這個可憐的人吧,幫助他計算一下,他可以收到至少一份offer的最大概率。(如果Speakless選擇了多個學校,得到任意一個學校的offer都可以)。
Input
輸入有若干組數據,每組數據的第一行有兩個正整數n,m(0<=n<=10000,0<=m<=1000)
后面的m行,每行都有兩個數據ai(整型),bi(實型)分別表示第i個學校的申請費用和可能拿到offer的概率。
輸入的最后有兩個0。
Output
每組數據都對應一個輸出,表示Speakless可能得到至少一份offer的最大概率。用百分數表示,精確到小數點后一位。
Sample Input
10 3
4 0.1
4 0.2
5 0.3
0 0
Sample Output
44.0%
Hint
You should use printf("%%") to print a '%'.
Author
Speakless
Source
Recommend
JGShining
#include<stdio.h>
double dp[10005];
int main()
{
int n,m,ai;
double bi;
int i,j;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
if(n==0&&m==0) break;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
dp[i]=0;
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%lf",&ai,&bi);
for(i=n;i>=ai;i--)
{
if(dp[i]<1-(1-dp[i-ai])*(1-bi))
dp[i]=1-(1-dp[i-ai])*(1-bi);
}
}
printf("%.1lf%%\n",dp[n]*100);
}
return 0;
}
免費餡餅
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 9307 Accepted Submission(s): 3011
Problem Description
都說天上不會掉餡餅,但有一天gameboy正走在回家的小徑上,忽然天上掉下大把大把的餡餅。說來gameboy的人品實在是太好了,這餡餅別處都不掉,就掉落在他身旁的10米范圍內。餡餅如果掉在了地上當然就不能吃了,所以gameboy馬上卸下身上的背包去接。但由于小徑兩側都不能站人,所以他只能在小徑上接。由于gameboy平時老呆在房間里玩游戲,雖然在游戲中是個身手敏捷的高手,但在現實中運動神經特別遲鈍,每秒種只有在移動不超過一米的范圍內接住墜落的餡餅。現在給這條小徑如圖標上坐標:  為了使問題簡化,假設在接下來的一段時間里,餡餅都掉落在0-10這11個位置。開始時gameboy站在5這個位置,因此在第一秒,他只能接到4,5,6這三個位置中其中一個位置上的餡餅。問gameboy最多可能接到多少個餡餅?(假設他的背包可以容納無窮多個餡餅)
Input
輸入數據有多組。每組數據的第一行為以正整數n(0<n<100000),表示有n個餡餅掉在這條小徑上。在結下來的n行中,每行有兩個整數x,T(0<T<100000),表示在第T秒有一個餡餅掉在x點上。同一秒鐘在同一點上可能掉下多個餡餅。n=0時輸入結束。
Output
每一組輸入數據對應一行輸出。輸出一個整數m,表示gameboy最多可能接到m個餡餅。
提示:本題的輸入數據量比較大,建議用scanf讀入,用cin可能會超時。
Sample Input
6
5 1
4 1
6 1
7 2
7 2
8 3
0
Sample Output
Author
lwg
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int dp[100005][12];
int main()
{
int n,i,j,maxt;
int x,t;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
maxt=0;
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&t);
dp[t][x]++;
if(maxt<t) maxt=t;
}
for(i=maxt-1;i>=0;i--)
{
dp[i][0]+=max(dp[i+1][1],dp[i+1][0]);
for(j=1;j<11;j++)
{
dp[i][j]+=max(max(dp[i+1][j-1],dp[i+1][j]),dp[i+1][j+1]);
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[0][5]);
}
return 0;
}
Tickets
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 385 Accepted Submission(s): 192
Problem Description
Jesus, what a great movie! Thousands of people are rushing to the cinema. However, this is really a tuff time for Joe who sells the film tickets. He is wandering when could he go back home as early as possible.
A good approach, reducing the total time of tickets selling, is let adjacent people buy tickets together. As the restriction of the Ticket Seller Machine, Joe can sell a single ticket or two adjacent tickets at a time.
Since you are the great JESUS, you know exactly how much time needed for every person to buy a single ticket or two tickets for him/her. Could you so kind to tell poor Joe at what time could he go back home as early as possible? If so, I guess Joe would full of appreciation for your help.
Input
There are N(1<=N<=10) different scenarios, each scenario consists of 3 lines:
1) An integer K(1<=K<=2000) representing the total number of people;
2) K integer numbers(0s<=Si<=25s) representing the time consumed to buy a ticket for each person;
3) (K-1) integer numbers(0s<=Di<=50s) representing the time needed for two adjacent people to buy two tickets together.
Output
For every scenario, please tell Joe at what time could he go back home as early as possible. Every day Joe started his work at 08:00:00 am. The format of time is HH:MM:SS am|pm.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
JGShining
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=2010;
int a[MAXN];//存放單個人買票的時間
int b[MAXN];//存放兩個相鄰的人一起買票的時間
int dp[MAXN];//dp[i]表示前i個人買票需要的最少時間
int main()
{
//freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("test.out","w",stdout);
int T,n,i,j;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
dp[0]=0;
dp[1]=a[1];
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
dp[i]=min(dp[i-1]+a[i],dp[i-2]+b[i]);
int h=dp[n]/60/60+8;
int m=dp[n]/60%60;
int s=dp[n]%60;
char hh[3],mm[3],ss[3];
hh[0]=h/10+'0';hh[1]=h%10+'0';hh[2]='\0';
mm[0]=m/10+'0';mm[1]=m%10+'0';mm[2]='\0';
ss[0]=s/10+'0';ss[1]=s%10+'0';ss[2]='\0';
if(h<=12) printf("%s:%s:%s am\n",hh,mm,ss);
else printf("%s:%s:%s pm\n",hh,mm,ss);
}
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=2010;
int a[MAXN];//存放單個人買票的時間
int b[MAXN];//存放兩個相鄰的人一起買票的時間
int dp[MAXN];//dp[i]表示前i個人買票需要的最少時間
int main()
{
//freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("test.out","w",stdout);
int T,n,i,j;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
dp[0]=0;
dp[1]=a[1];
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
dp[i]=min(dp[i-1]+a[i],dp[i-2]+b[i]);
int h=dp[n]/60/60+8;
int m=dp[n]/60%60;
int s=dp[n]%60;
/*char hh[3],mm[3],ss[3];
hh[0]=h/10+'0';hh[1]=h%10+'0';hh[2]='\0';
mm[0]=m/10+'0';mm[1]=m%10+'0';mm[2]='\0';
ss[0]=s/10+'0';ss[1]=s%10+'0';ss[2]='\0';
if(h<=12) printf("%s:%s:%s am\n",hh,mm,ss);
else printf("%s:%s:%s pm\n",hh,mm,ss);*/
/*或者用下面的方法輸出前面加iomanip頭文件 */
if(h<=12)
cout<<setfill('0')<<setw(2)<<h<<":"<<setfill('0')<<setw(2)<<m<<":"<<setfill('0')<<setw(2)<<s<<" am"<<endl;
else
cout<<setfill('0')<<setw(2)<<h<<":"<<setfill('0')<<setw(2)<<m<<":"<<setfill('0')<<setw(2)<<s<<" pm"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Eddy's picture
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2454 Accepted Submission(s): 1184
Problem Description
Eddy begins to like painting pictures recently ,he is sure of himself to become a painter.Every day Eddy draws pictures in his small room, and he usually puts out his newest pictures to let his friends appreciate. but the result it can be imagined, the friends are not interested in his picture.Eddy feels very puzzled,in order to change all friends 's view to his technical of painting pictures ,so Eddy creates a problem for the his friends of you.
Problem descriptions as follows: Given you some coordinates pionts on a drawing paper, every point links with the ink with the straight line, causes all points finally to link in the same place. How many distants does your duty discover the shortest length which the ink draws?
Input
The first line contains 0 < n <= 100, the number of point. For each point, a line follows; each following line contains two real numbers indicating the (x,y) coordinates of the point.
Input contains multiple test cases. Process to the end of file.
Output
Your program prints a single real number to two decimal places: the minimum total length of ink lines that can connect all the points.
Sample Input
3
1.0 1.0
2.0 2.0
2.0 4.0
Sample Output
Author
eddy
Recommend
JGShining
/*
HDU1162 Eddy's picture
題意:給定畫上n個點,求最短的線段把所有點連起來,簡單的最小生成樹
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAXN 110
struct Node//定義點
{
double x,y;
}node[MAXN];
double cost[MAXN][MAXN];//耗費矩陣
double distance(Node a,Node b)//兩點的距離
{
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
//***********************************************************************
//套用prim模板
//***********************************************************************
#define typec double
const typec INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int vis[MAXN];
typec lowc[MAXN];
typec prim(typec cost[][MAXN],int n)//點從0~n-1
{
int i,j,p;
typec minc,res=0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
vis[0]=1;
for(i=1;i<n;i++) lowc[i]=cost[0][i];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
minc=INF;
p=-1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(vis[j]==0&&minc>lowc[j])
{minc=lowc[j];p=j;}
if(minc==INF)return -1;//原圖不連通
res+=minc;vis[p]=1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(vis[j]==0&&lowc[j]>cost[p][j])
lowc[j]=cost[p][j];
}
return res;
}
//********************************************************************
int main()
{
int i,j,n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&node[i].x,&node[i].y);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i==j)cost[i][j]=0;
else
cost[i][j]=distance(node[i],node[j]);
}
printf("%.2lf\n",prim(cost,n));
}
return 0;
}
Jungle Roads
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1728 Accepted Submission(s): 1254
Problem Description
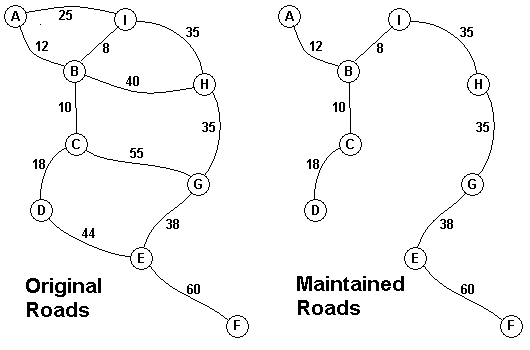 The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems. The input consists of one to 100 data sets, followed by a final line containing only 0. Each data set starts with a line containing only a number n, which is the number of villages, 1 < n < 27, and the villages are labeled with the first n letters of the alphabet, capitalized. Each data set is completed with n-1 lines that start with village labels in alphabetical order. There is no line for the last village. Each line for a village starts with the village label followed by a number, k, of roads from this village to villages with labels later in the alphabet. If k is greater than 0, the line continues with data for each of the k roads. The data for each road is the village label for the other end of the road followed by the monthly maintenance cost in aacms for the road. Maintenance costs will be positive integers less than 100. All data fields in the row are separated by single blanks. The road network will always allow travel between all the villages. The network will never have more than 75 roads. No village will have more than 15 roads going to other villages (before or after in the alphabet). In the sample input below, the first data set goes with the map above. The output is one integer per line for each data set: the minimum cost in aacms per month to maintain a road system that connect all the villages. Caution: A brute force solution that examines every possible set of roads will not finish within the one minute time limit.
Sample Input
9
A 2 B 12 I 25
B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8
C 2 D 18 G 55
D 1 E 44
E 2 F 60 G 38
F 0
G 1 H 35
H 1 I 35
3
A 2 B 10 C 40
B 1 C 20
0
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
Eddy
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 27
int map[MAXN][MAXN];
//*******************************************************
//最小生成樹模板
//*******************************************************
#define typec int
const typec INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int vis[MAXN];
typec lowc[MAXN];
typec prim(typec cost[][MAXN],int n)
{
int i,j,p;
typec minc,res=0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
vis[0]=1;
for(i=1;i<n;i++) lowc[i]=cost[0][i];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
minc=INF;
p=-1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(vis[j]==0&&minc>lowc[j])
{
minc=lowc[j];
p=j;
}
if(minc==INF)return -1;
res+=minc;
vis[p]=1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(vis[j]==0&&lowc[j]>cost[p][j])
lowc[j]=cost[p][j];
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,n;
int t,v;
char a,b;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i==j) map[i][j]=0;
else map[i][j]=INF;
}
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>b>>v;
map[a-'A'][b-'A']=v;
map[b-'A'][a-'A']=v;
}
}
printf("%d\n",prim(map,n));
}
return 0;
}
Arbitrage
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1186 Accepted Submission(s): 547
Problem Description
Arbitrage is the use of discrepancies in currency exchange rates to transform one unit of a currency into more than one unit of the same currency. For example, suppose that 1 US Dollar buys 0.5 British pound, 1 British pound buys 10.0 French francs, and 1 French franc buys 0.21 US dollar. Then, by converting currencies, a clever trader can start with 1 US dollar and buy 0.5 * 10.0 * 0.21 = 1.05 US dollars, making a profit of 5 percent.
Your job is to write a program that takes a list of currency exchange rates as input and then determines whether arbitrage is possible or not.
Input
The input file will contain one or more test cases. Om the first line of each test case there is an integer n (1<=n<=30), representing the number of different currencies. The next n lines each contain the name of one currency. Within a name no spaces will appear. The next line contains one integer m, representing the length of the table to follow. The last m lines each contain the name ci of a source currency, a real number rij which represents the exchange rate from ci to cj and a name cj of the destination currency. Exchanges which do not appear in the table are impossible.
Test cases are separated from each other by a blank line. Input is terminated by a value of zero (0) for n.
Output
For each test case, print one line telling whether arbitrage is possible or not in the format "Case case: Yes" respectively "Case case: No".
Sample Input
3
USDollar
BritishPound
FrenchFranc
3
USDollar 0.5 BritishPound
BritishPound 10.0 FrenchFranc
FrenchFranc 0.21 USDollar
3
USDollar
BritishPound
FrenchFranc
6
USDollar 0.5 BritishPound
USDollar 4.9 FrenchFranc
BritishPound 10.0 FrenchFranc
BritishPound 1.99 USDollar
FrenchFranc 0.09 BritishPound
FrenchFranc 0.19 USDollar
0
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
Eddy
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
map<string,int>name;
#define MAXN 30
double g[MAXN][MAXN];
//*****************************************************
//Floyed算法,求任意兩個頂點間的最短路徑
//dis[][]記錄任意兩點間的最短路徑,初始的dis[][]記錄直接路徑
//*****************************************************
#define typec double
void floyed(typec dis[][MAXN],int n)//節點從1~n編號
{
int i,j,k;
for(k=1;k<=n;k++)
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(dis[i][j]<dis[i][k]*dis[k][j])
dis[i][j]=dis[i][k]*dis[k][j];
}
//**********************************************************
int main()
{
int n,i,m,j;
string str1,str2;
double r;
int iCase=0;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
iCase++;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>str1;
name[str1]=i;
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(i==j)g[i][j]=1;
else g[i][j]=0;
}
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
cin>>str1>>r>>str2;
g[name[str1]][name[str2]]=r;
}
floyed(g,n);
bool flag=false;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(g[i][i]>1)
{flag=true;break;}
if(flag) printf("Case %d: Yes\n",iCase);
else printf("Case %d: No\n",iCase);
}
return 0;
}
A Walk Through the Forest
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2121 Accepted Submission(s): 756
Problem Description
Jimmy experiences a lot of stress at work these days, especially since his accident made working difficult. To relax after a hard day, he likes to walk home. To make things even nicer, his office is on one side of a forest, and his house is on the other. A nice walk through the forest, seeing the birds and chipmunks is quite enjoyable.
The forest is beautiful, and Jimmy wants to take a different route everyday. He also wants to get home before dark, so he always takes a path to make progress towards his house. He considers taking a path from A to B to be progress if there exists a route from B to his home that is shorter than any possible route from A. Calculate how many different routes through the forest Jimmy might take.
Input
Input contains several test cases followed by a line containing 0. Jimmy has numbered each intersection or joining of paths starting with 1. His office is numbered 1, and his house is numbered 2. The first line of each test case gives the number of intersections N, 1 < N ≤ 1000, and the number of paths M. The following M lines each contain a pair of intersections a b and an integer distance 1 ≤ d ≤ 1000000 indicating a path of length d between intersection a and a different intersection b. Jimmy may walk a path any direction he chooses. There is at most one path between any pair of intersections.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer indicating the number of different routes through the forest. You may assume that this number does not exceed 2147483647
Sample Input
5 6
1 3 2
1 4 2
3 4 3
1 5 12
4 2 34
5 2 24
7 8
1 3 1
1 4 1
3 7 1
7 4 1
7 5 1
6 7 1
5 2 1
6 2 1
0
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
Eddy
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1005
int cost[MAXN][MAXN];
int dis[MAXN];
int sum[MAXN];//記錄路徑數
//*************************************************************
//Dijkstra-----數組實現
//單源最短路徑
//cost[i][j]為i,j間的距離
//lowcost[]————從點beg到其他點的最近距離
//path[]---------beg為根展開的樹,記錄父親結點
//*************************************************************
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f //這個無窮大不能太大,小心后面相加時溢出
#define typec int //定義需要的數據類型
int path[MAXN],vis[MAXN];
void Dijkstra(typec cost[][MAXN],typec lowcost[MAXN],int n,int beg)
//結點是1~n標記的
{
int i,j;
typec minc;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
vis[beg]=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
lowcost[i]=cost[beg][i];path[i]=beg;
}
lowcost[beg]=0;
path[beg]=-1;//樹根的標記
int pre;
for(int num=2;num<n;num++)//決定從pre出發的n-1個最短路
{
minc=INF;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(vis[j]==0&&lowcost[j]<minc)
{pre=j;minc=lowcost[j];}
if(minc>=INF)break;
vis[pre]=1;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(vis[j]==0&&lowcost[pre]+cost[pre][j]<lowcost[j])
{lowcost[j]=lowcost[pre]+cost[pre][j];path[j]=pre;}
}
}
//**********************************************************************
int dfs(int i,int n)//記憶性搜索,類似于動態規劃的方法,記錄下來
{
if(i==2) return 1;
if(sum[i]!=-1) return sum[i];
int cnt=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(cost[i][j]<INF&&dis[j]<dis[i])
cnt+=dfs(j,n);
}
sum[i]=cnt;
return sum[i];
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
int n,m;
int a,b,d;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
scanf("%d",&m);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(i==j)cost[i][j]=0;
else cost[i][j]=INF;
}
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&d);
cost[a][b]=d;
cost[b][a]=d;
}
Dijkstra(cost,dis,n,2);
memset(sum,-1,sizeof(sum));
printf("%d\n",dfs(1,n));
}
}
寒冰王座
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4537 Accepted Submission(s): 2151
Problem Description
不死族的巫妖王發工資拉,死亡騎士拿到一張N元的鈔票(記住,只有一張鈔票),為了防止自己在戰斗中頻繁的死掉,他決定給自己買一些道具,于是他來到了地精商店前.
死亡騎士:"我要買道具!"
地精商人:"我們這里有三種道具,血瓶150塊一個,魔法藥200塊一個,無敵藥水350塊一個."
死亡騎士:"好的,給我一個血瓶."
說完他掏出那張N元的大鈔遞給地精商人.
地精商人:"我忘了提醒你了,我們這里沒有找客人錢的習慣的,多的錢我們都當小費收了的,嘿嘿."
死亡騎士:"......"
死亡騎士想,與其把錢當小費送個他還不如自己多買一點道具,反正以后都要買的,早點買了放在家里也好,但是要盡量少讓他賺小費.
現在死亡騎士希望你能幫他計算一下,最少他要給地精商人多少小費.
Input
輸入數據的第一行是一個整數T(1<=T<=100),代表測試數據的數量.然后是T行測試數據,每個測試數據只包含一個正整數N(1<=N<=10000),N代表死亡騎士手中鈔票的面值.
注意:地精商店只有題中描述的三種道具.
Output
對于每組測試數據,請你輸出死亡騎士最少要浪費多少錢給地精商人作為小費.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Author
Ignatius.L
Recommend
Ignatius.L
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAXN 10000
int c1[MAXN],c2[MAXN];
int v[3];
void mufun(int sum,int *v)
{
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<=MAXN;i+=v[0])
c1[i]=1;
for(k=1;k<sum;k++)
{
for(i=0;i<=MAXN;i++)
{
for(j=0;i+j<=MAXN;j+=v[k])
c2[i+j]+=c1[i];
}
for(i=0;i<=MAXN;i++)
{
c1[i]=c2[i];
c2[i]=0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n,T;
v[0]=150;
v[1]=200;
v[2]=350;
memset(c1,0,sizeof(c1));
memset(c2,0,sizeof(c2));
mufun(3,v);
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int cnt=0;
while(c1[n-cnt]==0)
{
cnt++;
}
printf("%d\n",cnt);
}
return 0;
}
Reverse Number
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2047 Accepted Submission(s): 926
Problem Description
Welcome to 2006'4 computer college programming contest!
Specially, I give my best regards to all freshmen! You are the future of HDU ACM! And now, I must tell you that ACM problems are always not so easy, but, except this one... Ha-Ha!
Give you an integer; your task is to output its reverse number. Here, reverse number is defined as follows:
1. The reverse number of a positive integer ending without 0 is general reverse, for example, reverse (12) = 21;
2. The reverse number of a negative integer is negative, for example, reverse (-12) = -21;
3. The reverse number of an integer ending with 0 is described as example, reverse (1200) = 2100.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases. There is a positive integer n (n<100) in the first line, which means the number of test cases, and then n 32-bit integers follow.
Output
For each test case, you should output its reverse number, one case per line.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Author
lcy
Source
Recommend
lxj
/*
HDU 1266
水題,但是要用字符串去存儲,并不像題目說的是整型的
數據很大
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char m[100];
long long x;
int T,i;
int t;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%s",&m);
int k=strlen(m);
for(t=k-1;t>=0;t--)
if(m[t]!='0') break;
if(m[0]=='-')
{
printf("-");
for(i=t;i>=1;i--)
printf("%c",m[i]);
for(i=t+1;i<k;i++)
printf("0");
}
else
{
for(i=t;i>=0;i--)
printf("%c",m[i]);
for(i=t+1;i<k;i++)
printf("0");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
|
|
| | 日 | 一 | 二 | 三 | 四 | 五 | 六 |
|---|
| 31 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 1 | 2 | 3 | | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|
公告
導航
統計
- 隨筆: 100
- 文章: 0
- 評論: 2
- 引用: 0
常用鏈接
留言簿(2)
隨筆分類
隨筆檔案
博客
搜索
最新評論

閱讀排行榜
評論排行榜
|
|