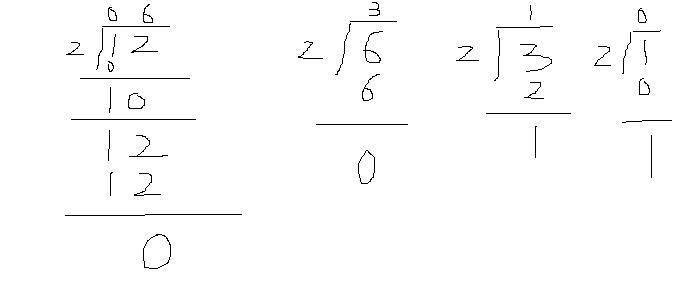Proud Merchants
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/65536 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
Recently, iSea went to an ancient country. For such a long time, it was the most wealthy and powerful kingdom in the world. As a result, the people in this country are still very proud even if their nation hasn’t been so wealthy any more.
Input
There are several test cases in the input.
Output
For each test case, output one integer, indicating maximum value iSea could get.
Sample Input
2 10
10 15 10
5 10 5
3 10
5 10 5
3 5 6
2 7 3
Sample Output
Author
iSea @ WHU
Source
Recommend
zhouzeyong
這是一道01背包的變形題,題目增加了一個限制條件,即當你所擁有的錢數大于某個限定值時才可以購買該物品。
按照q - p以由大到小的順序排序,然后進行01背包的DP即可。
#include < stdio.h > < algorithm > < iostream > using namespace std; const int MAXN = 5005 ; int dp[MAXN]; struct Node int p,q,v; 505 ]; bool cmp(Node a,Node b) return (a.q - a.p) < (b.q - b.p); int main() int n,m; int i,j; int p,q,v; while (scanf( " %d%d " , & n, & m) != EOF) for (i = 0 ;i <= m;i ++ ) = 0 ; for (i = 0 ;i < n;i ++ ) " %d%d%d " , & node[i].p, & node[i].q, & node[i].v); + n,cmp); for (i = 0 ;i < n;i ++ ) for (j = m;j >= node[i].p;j -- ) if (j >= node[i].q) = max(dp[j],dp[j - node[i].p] + node[i].v); int ans = 0 ; for (i = 1 ;i <= m;i ++ ) if (ans < dp[i]) ans = dp[i]; " %d\n " ,ans); return 0 ;
過山車
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
RPG girls今天和大家一起去游樂場玩,終于可以坐上夢寐以求的過山車了。可是,過山車的每一排只有兩個座位,而且還有條不成文的規矩,就是每個女生必須找個個男生做partner和她同坐。但是,每個女孩都有各自的想法,舉個例子把,Rabbit只愿意和XHD或PQK做partner,Grass只愿意和linle或LL做partner,PrincessSnow愿意和水域浪子或偽酷兒做partner。考慮到經費問題,boss劉決定只讓找到partner的人去坐過山車,其他的人,嘿嘿,就站在下面看著吧。聰明的Acmer,你可以幫忙算算最多有多少對組合可以坐上過山車嗎?
Input
輸入數據的第一行是三個整數K , M , N,分別表示可能的組合數目,女生的人數,男生的人數。0<K<=1000
Output
對于每組數據,輸出一個整數,表示可以坐上過山車的最多組合數。
Sample Input
6 3 3
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 3
3 1
0
Sample Output
Author
PrincessSnow
Source
Recommend
lcy
#include < stdio.h > < string .h > const int MAXN = 510 ; int uN,vN; // u,v數目 int g[MAXN][MAXN]; // 編號是0~n-1的 int linker[MAXN]; bool used[MAXN]; bool dfs( int u) int v; for (v = 1 ;v <= vN;v ++ ) if (g[u][v] &&! used[v]) = true ; if (linker[v] ==- 1 || dfs(linker[v])) = u; return true ; return false ; int hungary() int res = 0 ; int u; - 1 , sizeof (linker)); for (u = 1 ;u <= uN;u ++ ) 0 , sizeof (used)); if (dfs(u)) res ++ ; return res; int main() int k; int u,v; while (scanf( " %d " , & k),k) " %d%d " , & uN, & vN); 0 , sizeof (g)); while (k -- ) " %d%d " , & u, & v); = 1 ; " %d\n " ,hungary()); return 0 ;
前面的內容來源于:http://www.cnblogs.com/phinecos/archive/2009/09/11/1564975.html
引用原文:
在數據結構課關于棧的這一章中,我們都學過用 “ 模 2 取余法 ” 來將一個 10 進制數轉換為一個二進制數,進而可以推廣到 “ 模 n 取余法 ” ,經其轉換為 n 進制( n 任意指定)。
確實,這是一個很基礎的題目,可你是否想過如果這個 10 進制數是一個大數(其位數可能上千位,此時用一般數據類型肯定是會溢出的),那么這個問題又如何來求解呢?
當然,也許你會說很簡單嘛,自己寫一個大數類(當然至少要寫一個大數除法才行),或者你用的是 Java 這種現代化語言,就更輕松了,直接用 BigInteger 這樣的大數類就可以來表示一個大數,進而用書上教的方法來實現。
但是,真的需要用到大數類嗎?事實上, “ 殺雞焉用牛刀 “ ,我們在紙上模擬一番上述運算后就可以發現,只要做一些小小的改進,就可以在不使用大數的情況下,也可以通過 “ 模 n 取余 ” 的原理來實現大數的進制轉換的。(當然,整體的思想仍然是 “ 模 n 取余 ” 原理!!!)。
舉個簡單的例子,就比如說把 10 進制數 12 轉換為 2 進制形式,書上的方法可以用下圖來表示
按照 “ 先余為低位,后余為高位 “ 這條鐵律,其結果為 1100.
這是書上教我們的常規思路(可惜按這個的話,大數是沒法考慮的,因為假如這里不是12,而是一個1000位的大數,由于是是對大數的整體進行取余運算,不使用大數類及其除法操作,又如何得以進行呢?),可我們的目的是不使用大數類,那么現在我們就來換一個視角來看這個問題, 12 是一個十位數,十位上是 1 ,個位上是 2 ,按照我們正常的思維來看,這個計算應該是下面這樣的:
那么我們發現在第一輪運算時,十位上的 1 作為被除數, 2 作為除數,得到的商是 0 ,余數是 1( 可以斷言只考慮當前這一個數位的計算,余數或是 0 ,或是 1 ,若是 1 的話,則進入下一數位(這里即對個位進行運算)時,要用 1 乘上進制(這里是 10 )再加上下一個數位上的值(這里是 2 ) ) ,即得到運算進入個位時被除數是 12 ,除數是 2 ,得到的商是 6 ,余數是 0 。第一輪運算的結果是商是 06 ,余數是 0.
進入第二輪運算,則上一輪的商 6 (這里首先要去掉前面多余的 0 )變成本輪的被除數,如此下去,即可得到每輪的余數。
推廣開來,如果被除數是一個 1000 位的大數,例如 “12343435154324123……342314324343”
那么我們照樣可以從第一個數位開始逐位考慮,比如第一位是 1 (作為被除數), 2 是除數,得到的商是 0 ,余數是 1 ,然后是第二個數位 2 ,由于上一位留下了余數 1 ,則此時被除數應該是 1*10+2 = 12, 所以得到的商是 6 ,余數是 0 ,即運算到此時的商是 06 ,然后是第三個數位 3 ,由于上一個數位留下的余數是 0 ,所以此時被除數就是 3 ,。。。如此下去就完成第一輪的運算,
這一輪完畢后,需要把得到的商變成下一輪的被除數,繼續上述的運算,直到被除數為 0 才停止。
下面給出了一個示例代碼,展示了如何將一個10進制的大數轉換為其二進制形式,僅供參考:
#include < stdio.h > < string .h > char str[ 1000 ]; // 輸入字符串 int start[ 1000 ],ans[ 1000 ],res[ 1000 ]; // 被除數,商,余數 // 轉換前后的進制 const int oldBase = 10 ; const int newBase = 2 ; void change() // 各個數位還原為數字形式 int i,len = strlen(str); 0 ] = len; for (i = 1 ;i <= len;i ++ ) if (str[i - 1 ] >= ' 0 ' && str[i - 1 ] <= ' 9 ' ) = str[i - 1 ] - ' 0 ' ; void solve() 0 , sizeof (res)); // 余數初始化為空 int y,i,j; // 模n取余法,(總體規律是先余為低位,后余為高位) while (start[ 0 ] >= 1 ) // 只要被除數仍然大于等于1,那就繼續“模2取余” y = 0 ; = 1 ; 0 ] = start[ 0 ]; // while (i <= start[ 0 ]) = y * oldBase + start[i]; ++ ] = y / newBase; %= newBase; ++ res[ 0 ]] = y; // 這一輪運算得到的余數 i = 1 ; // 找到下一輪商的起始處 while ((i <= ans[ 0 ]) && (ans[i] == 0 )) i ++ ; // 清除這一輪使用的被除數 memset(start, 0 , sizeof (start)); // 本輪得到的商變為下一輪的被除數 for (j = i;j <= ans[ 0 ];j ++ ) ++ start[ 0 ]] = ans[j]; 0 , sizeof (ans)); // 清除這一輪的商,為下一輪運算做準備 } void output() // 從高位到低位逆序輸出 int i; for (i = res[ 0 ];i >= 1 ; -- i) " %d " ,res[i]); " \n " ); int main() " %s " ,str); return 0 ;
個人根據POJ1220,總結高精度的N進制轉換模板如下:
/* */ < stdio.h > < string .h > 1000 char str[MAXSIZE]; // 輸入字符串 int start[MAXSIZE],ans[MAXSIZE],res[MAXSIZE]; // 被除數,商,余數 int oleBasw,newBase; // 轉換前后的進制 // 單個字符得到數字 int getNum( char c) // 這里進制字符是先數字,后大寫字母,后小寫字母的 { if (c >= ' 0 ' && c <= ' 9 ' ) return c - ' 0 ' ; // 數字 if (c >= ' A ' && c >= ' Z ' ) return c - ' A ' + 10 ; // 大寫字母 return c - ' a ' + 36 ; // 小寫字母 } // 數字得到字符 char getChar( int i) if (i >= 0 && i <= 9 ) return i + ' 0 ' ; if (i >= 10 && i <= 35 ) return i - ' 10 ' + ' A ' ; return i - 36 + ' a ' ; void change() // 把輸入的字符串的各個數位還原為數字形式 { int i; 0 ] = strlen(str); // 數組的0位存的是數組長度 for (i = 1 ;i <= start[ 0 ];i ++ ) = getNum(str[i - 1 ]); void solve() 0 , sizeof (res)); // 余數位初始化為空 int y,i,j; while (start[ 0 ] >= 1 ) = 0 ;i = 1 ; 0 ] = start[ 0 ]; while (i <= start[ 0 ]) = y * oldBase + start[i]; ++ ] = y / newBase; %= newBase; ++ res[ 0 ]] = y; // 這一輪得到的余數 i = 1 ; // 找下一輪商的起始處,去掉前面的0 while (i <= ans[ 0 ] && ans[i] == 0 ) i ++ ; 0 , sizeof (start)); for (j = i;j < ans[ 0 ];j ++ ) ++ start[ 0 ]] = ans[j]; 0 , sizeof (ans)); void output() // 從高位到低位逆序輸出 { int i; for (i = res[ 0 ];i >= 1 ;i -- ) " %d " ,getChar(res[i])); " \n " );
NUMBER BASE CONVERSION
Time Limit: 1000MSMemory Limit: 10000K
Total Submissions: 3231Accepted: 1394
Description
Write a program to convert numbers in one base to numbers in a second base. There are 62 different digits:
Input
The first line of input contains a single positive integer. This is the number of lines that follow. Each of the following lines will have a (decimal) input base followed by a (decimal) output base followed by a number expressed in the input base. Both the input base and the output base will be in the range from 2 to 62. That is (in decimal) A = 10, B = 11, ..., Z = 35, a = 36, b = 37, ..., z = 61 (0-9 have their usual meanings).
Output
The output of the program should consist of three lines of output for each base conversion performed. The first line should be the input base in decimal followed by a space then the input number (as given expressed in the input base). The second output line should be the output base followed by a space then the input number (as expressed in the output base). The third output line is blank.
Sample Input
8
62 2 abcdefghiz
10 16 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890
16 35 3A0C92075C0DBF3B8ACBC5F96CE3F0AD2
35 23 333YMHOUE8JPLT7OX6K9FYCQ8A
23 49 946B9AA02MI37E3D3MMJ4G7BL2F05
49 61 1VbDkSIMJL3JjRgAdlUfcaWj
61 5 dl9MDSWqwHjDnToKcsWE1S
5 10 42104444441001414401221302402201233340311104212022133030
Sample Output
62 abcdefghiz
2 11011100000100010111110010010110011111001001100011010010001
10 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890
16 3A0C92075C0DBF3B8ACBC5F96CE3F0AD2
16 3A0C92075C0DBF3B8ACBC5F96CE3F0AD2
35 333YMHOUE8JPLT7OX6K9FYCQ8A
35 333YMHOUE8JPLT7OX6K9FYCQ8A
23 946B9AA02MI37E3D3MMJ4G7BL2F05
23 946B9AA02MI37E3D3MMJ4G7BL2F05
49 1VbDkSIMJL3JjRgAdlUfcaWj
49 1VbDkSIMJL3JjRgAdlUfcaWj
61 dl9MDSWqwHjDnToKcsWE1S
61 dl9MDSWqwHjDnToKcsWE1S
5 42104444441001414401221302402201233340311104212022133030
5 42104444441001414401221302402201233340311104212022133030
10 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890
Source
/* */ < stdio.h > < string .h > #define MAXSIZE 1000 char str[MAXSIZE]; // 輸入字符串 int start[MAXSIZE],ans[MAXSIZE],res[MAXSIZE]; // 被除數,商,余數 int oldBase,newBase; // 轉換前后的進制 // 單個字符得到數字 int getNum( char c) // 這里進制字符是先數字,后大寫字母,后小寫字母的 { if (c >= ' 0 ' && c <= ' 9 ' ) return c - ' 0 ' ; // 數字 if (c >= ' A ' && c <= ' Z ' ) return c - ' A ' + 10 ; // 大寫字母 return c - ' a ' + 36 ; // 小寫字母 } // 數字得到字符 char getChar( int i) if (i >= 0 && i <= 9 ) return i + ' 0 ' ; if (i >= 10 && i <= 35 ) return i - 10 + ' A ' ; return i - 36 + ' a ' ; void change() // 把輸入的字符串的各個數位還原為數字形式 { int i; 0 ] = strlen(str); // 數組的0位存的是數組長度 for (i = 1 ;i <= start[ 0 ];i ++ ) = getNum(str[i - 1 ]); void solve() 0 , sizeof (res)); // 余數位初始化為空 int y,i,j; while (start[ 0 ] >= 1 ) = 0 ;i = 1 ; 0 ] = start[ 0 ]; while (i <= start[ 0 ]) = y * oldBase + start[i]; ++ ] = y / newBase; %= newBase; ++ res[ 0 ]] = y; // 這一輪得到的余數 i = 1 ; // 找下一輪商的起始處,去掉前面的0 while (i <= ans[ 0 ] && ans[i] == 0 ) i ++ ; 0 , sizeof (start)); for (j = i;j <= ans[ 0 ];j ++ ) ++ start[ 0 ]] = ans[j]; 0 , sizeof (ans)); void output() // 從高位到低位逆序輸出 { int i; " %d %s\n " ,oldBase,str); " %d " ,newBase); for (i = res[ 0 ];i >= 1 ;i -- ) " %c " ,getChar(res[i])); " \n\n " ); int main() // freopen("test.in","r",stdin); // freopen("test.out","w",stdout); int T; " %d " , & T); while (T -- ) " %d %d %s " , & oldBase, & newBase,str); return 0 ;
一、 最大匹配——匈牙利算法
/* *************************************************** */ const int MAXN = 1000 ; int uN,vN; // u,v數目 int g[MAXN][MAXN]; // 編號是0~n-1的 int linker[MAXN]; bool used[MAXN]; bool dfs( int u) int v; for (v = 0 ;v < vN;v ++ ) if (g[u][v] &&! used[v]) = true ; if (linker[v] ==- 1 || dfs(linker[v])) = u; return true ; return false ; int hungary() int res = 0 ; int u; - 1 , sizeof (linker)); for (u = 0 ;u < uN;u ++ ) 0 , sizeof (used)); if (dfs(u)) res ++ ; return res;
簡單例子:
HDU 2063 過山車
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
const int MAXN=510;
int uN,vN; //u,v 數目
int g[MAXN][MAXN];// 編號是 0~n-1 的
int linker[MAXN];
bool used[MAXN];
bool dfs(int u)
{
int v;
for(v=1;v<=vN;v++)
if(g[u][v]&&!used[v])
{
used[v]=true;
if(linker[v]==-1||dfs(linker[v]))
{
linker[v]=u;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int hungary()
{
int res=0;
int u;
memset(linker,-1,sizeof(linker));
for(u=1;u<=uN;u++)
{
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
if(dfs(u)) res++;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int k;
int u,v;
while(scanf("%d",&k),k)
{
scanf("%d%d",&uN,&vN);
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
while(k--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
g[u][v]=1;
}
printf("%d\n",hungary());
}
return 0;
}
例: HDU 1045 Fire Net
/*
HDU 1045
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int uN,vN;
int g[20][20];
int linker[20];
bool used[20];
char map[5][5];
int mapr[5][5];
int mapl[5][5];
bool dfs(int u)
{
int v;
for(v=1;v<=vN;v++)
if(g[u][v]&&!used[v])
{
used[v]=true;
if(linker[v]==-1||dfs(linker[v]))
{
linker[v]=u;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int hungary()
{
int res=0;
int u;
memset(linker,-1,sizeof(linker));
for(u=1;u<=uN;u++)
{
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
if(dfs(u)) res++;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,n;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
memset(mapl,0,sizeof(mapl));
memset(mapr,0,sizeof(mapr));
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
cin>>map[i][j];
if(map[i][j]=='X')
mapl[i][j]=mapr[i][j]=-1;
}
int p1=0;
uN=0;vN=0;
//給行編號
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
while(mapr[i][j]==-1&&j<=n)
j++;
p1++;
while(mapr[i][j]!=-1&&j<=n)
{
mapr[i][j]=p1;
if(uN<p1) uN=p1;
j++;
}
}
int p2=0;
//給列編號
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
while(mapl[i][j]==-1&&i<=n)
i++;
p2++;
while(mapl[i][j]!=-1&&i<=n)
{
mapl[i][j]=p2;
if(vN<p2) vN=p2;
i++;
}
}
//建圖
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(mapr[i][j]!=-1&&mapl[i][j]!=-1)
g[mapr[i][j]][mapl[i][j]]=1;
}
printf("%d\n",hungary());
}
return 0;
}
Fire Net
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
Suppose that we have a square city with straight streets. A map of a city is a square board with n rows and n columns, each representing a street or a piece of wall.
A blockhouse is a small castle that has four openings through which to shoot. The four openings are facing North, East, South, and West, respectively. There will be one machine gun shooting through each opening.
Here we assume that a bullet is so powerful that it can run across any distance and destroy a blockhouse on its way. On the other hand, a wall is so strongly built that can stop the bullets.
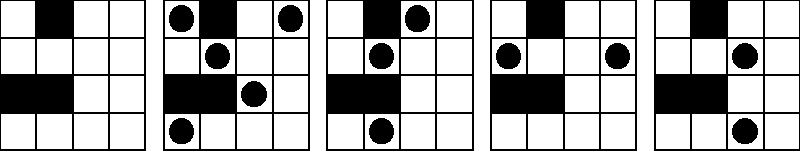
The goal is to place as many blockhouses in a city as possible so that no two can destroy each other. A configuration of blockhouses is legal provided that no two blockhouses are on the same horizontal row or vertical column in a map unless there is at least one wall separating them. In this problem we will consider small square cities (at most 4x4) that contain walls through which bullets cannot run through.
The following image shows five pictures of the same board. The first picture is the empty board, the second and third pictures show legal configurations, and the fourth and fifth pictures show illegal configurations. For this board, the maximum number of blockhouses in a legal configuration is 5; the second picture shows one way to do it, but there are several other ways.
Your task is to write a program that, given a description of a map, calculates the maximum number of blockhouses that can be placed in the city in a legal configuration.
Input
The input file contains one or more map descriptions, followed by a line containing the number 0 that signals the end of the file. Each map description begins with a line containing a positive integer n that is the size of the city; n will be at most 4. The next n lines each describe one row of the map, with a '.' indicating an open space and an uppercase 'X' indicating a wall. There are no spaces in the input file.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing the maximum number of blockhouses that can be placed in the city in a legal configuration.
Sample Input
4 .X.. .... XX.. .... 2 XX .X 3 .X. X.X .X. 3 ... .XX .XX 4 .... .... .... .... 0
Sample Output
Source
/* */ < stdio.h > < string .h > < iostream > using namespace std; int uN,vN; int g[ 20 ][ 20 ]; int linker[ 20 ]; bool used[ 20 ]; char map[ 5 ][ 5 ]; int mapr[ 5 ][ 5 ]; int mapl[ 5 ][ 5 ]; bool dfs( int u) int v; for (v = 1 ;v <= vN;v ++ ) if (g[u][v] &&! used[v]) = true ; if (linker[v] ==- 1 || dfs(linker[v])) = u; return true ; return false ; int hungary() int res = 0 ; int u; - 1 , sizeof (linker)); for (u = 1 ;u <= uN;u ++ ) 0 , sizeof (used)); if (dfs(u)) res ++ ; return res; int main() int i,j,n; while (scanf( " %d " , & n),n) 0 , sizeof (mapl)); 0 , sizeof (mapr)); 0 , sizeof (g)); for (i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++ ) for (j = 1 ;j <= n;j ++ ) >> map[i][j]; if (map[i][j] == ' X ' ) = mapr[i][j] =- 1 ; int p1 = 0 ; = 0 ;vN = 0 ; // 給行編號 for (i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++ ) for (j = 1 ;j <= n;j ++ ) while (mapr[i][j] ==- 1 && j <= n) ++ ; ++ ; while (mapr[i][j] !=- 1 && j <= n) = p1; if (uN < p1) uN = p1; ++ ; int p2 = 0 ; // 給列編號 for (j = 1 ;j <= n;j ++ ) for (i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++ ) while (mapl[i][j] ==- 1 && i <= n) ++ ; ++ ; while (mapl[i][j] !=- 1 && i <= n) = p2; if (vN < p2) vN = p2; ++ ; // 建圖 for (i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++ ) for (j = 1 ;j <= n;j ++ ) if (mapr[i][j] !=- 1 && mapl[i][j] !=- 1 ) = 1 ; " %d\n " ,hungary()); return 0 ;
暴搜也能過的,附暴搜代碼:
/* */ < stdio.h > using namespace std; char map[ 5 ][ 5 ]; int maxnum; int n; bool Build( int row, int col) int i,j; for (i = row;i >= 0 ;i -- ) if (map[i][col] == ' O ' ) return false ; if (map[i][col] == ' X ' ) break ; for (j = col;j >= 0 ;j -- ) if (map[row][j] == ' O ' ) return false ; if (map[row][j] == ' X ' ) break ; return true ; void dfs( int i, int num) int row,col; if (i == n * n) if (num > maxnum) maxnum = num; return ; else = i / n; = i % n; if (map[row][col] == ' . ' && Build(row,col)) = ' O ' ; + 1 ,num + 1 ); = ' . ' ; + 1 ,num); int main() int i; while (scanf( " %d " , & n),n) = 0 ; for (i = 0 ;i < n;i ++ ) " %s " , & map[i]); 0 , 0 ); " %d\n " ,maxnum); return 0 ;
題目鏈接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2444
題意:
有 n 個學生,有 m 對人是認識的,每一對認識的人能分到一間房,問能否把 n 個學生分成兩部分,每部分內的學生互不認識,而兩部分之間的學生認識。如果可以分成兩部分,就算出房間最多需要多少間,否則就輸出 No 。
分析:
先是要判斷是否為二部圖,然后求最大匹配。
這里的程序 hungary() 用 vector 實現
/* */ < iostream > < string .h > < vector > using namespace std; #define MAXN 202 < int > EV[MAXN]; int linker[MAXN]; bool used[MAXN]; int uN; int matchs[MAXN],cnt[MAXN]; bool dfs( int u) int i; for (i = 0 ;i < EV[u].size();i ++ ) int v = EV[u][i]; if ( ! used[v]) = true ; if (linker[v] ==- 1 || dfs(linker[v])) = u; return true ; return false ; int hungary() int res = 0 ; int u; - 1 , sizeof (linker)); for (u = 1 ;u <= uN;u ++ ) false , sizeof (used)); if (dfs(u)) res ++ ; return res; bool judge( int x, int y) int i; for (i = 0 ;i < EV[x].size();i ++ ) if (cnt[EV[x][i]] == 0 ) =- 1 * y; = true ; if ( ! judge(EV[x][i], - 1 * y)) return false ; else if (cnt[EV[x][i]] == y) return false ; return true ; bool matched() int i; false , sizeof (matchs)); for (i = 1 ;i <= uN;i ++ ) if (EV[i].size() &&! matchs[i]) 0 , sizeof (cnt)); =- 1 ; = true ; if ( ! judge(i, - 1 )) return false ; return true ; int main() int m; int i; int u,v; while (scanf( " %d%d " , & uN, & m) != EOF) for (i = 1 ;i <= uN;i ++ ) if (EV[i].size()) EV[i].clear(); while (m -- ) " %d%d " , & u, & v); if (matched()) " %d\n " ,hungary() / 2 ); else printf( " No\n " ); return 0 ;
題目大意:
有p個課程和n個學生,每個學生可以自由選擇課程(0到p個),現在要建立一個委員會,問是否能找到每個課程都有學生代表的集合,一個學生只能代表一個課程
題目鏈接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1083
簡單的二分匹配,用匈牙利算法就可以,主要是練習模板,固定方法解題!
程序:
#include < stdio.h > < iostream > using namespace std; #define MAXN 305 int g[MAXN][MAXN]; int uN,vN; int linker[MAXN]; bool used[MAXN]; bool dfs( int u) int v; for (v = 1 ;v <= vN;v ++ ) if (g[u][v] &&! used[v]) = true ; if (linker[v] ==- 1 || dfs(linker[v])) = u; return true ; return false ; int hungary() int res = 0 ,u; - 1 , sizeof (linker)); for (u = 1 ;u <= uN;u ++ ) 0 , sizeof (used)); if (dfs(u)) res ++ ; return res; int main() int u,v; int T,i,n; " %d " , & T); while (T -- ) " %d%d " , & uN, & vN); 0 , sizeof (g)); for (u = 1 ;u <= uN;u ++ ) " %d " , & n); while (n -- ) " %d " , & v); = 1 ; if (uN == hungary()) printf( " YES\n " ); else printf( " NO\n " ); return 0 ;
不好意思,感覺太簡單了就沒有加注釋!!!匈牙利算法,詳解可以看我前面幾遍關于二分匹配的文章!
棋盤游戲
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 5 Accepted Submission(s) : 4
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
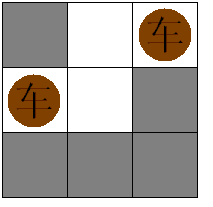
小希和Gardon在玩一個游戲:對一個N*M的棋盤,在格子里放盡量多的一些國際象棋里面的“車”,并且使得他們不能互相攻擊,這當然很簡單,但是Gardon限制了只有某些格子才可以放,小希還是很輕松的解決了這個問題(見下圖)注意不能放車的地方不影響車的互相攻擊。
所以現在Gardon想讓小希來解決一個更難的問題,在保證盡量多的“車”的前提下,棋盤里有些格子是可以避開的,也就是說,不在這些格子上放車,也可以保證盡量多的“車”被放下。但是某些格子若不放子,就無法保證放盡量多的“車”,這樣的格子被稱做重要點。Gardon想讓小希算出有多少個這樣的重要點,你能解決這個問題么?
Input
輸入包含多組數據,
Output
對輸入的每組數據,按照如下格式輸出:
Sample Input
3 3 4
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 2
3 3 4
1 2
1 3
2 1
3 2
Sample Output
Board 1 have 0 important blanks for 2 chessmen.
Board 2 have 3 important blanks for 3 chessmen.
Author
Gardon
Source
杭電ACM集訓隊訓練賽(VI)
代碼:
#include < stdio.h > < iostream > using namespace std; #define MAXN 105 int g[MAXN][MAXN]; int uN,vN; int linker[MAXN]; bool used[MAXN]; bool dfs( int u) int v; for (v = 1 ;v <= vN;v ++ ) if (g[u][v] &&! used[v]) = true ; if (linker[v] ==- 1 || dfs(linker[v])) = u; return true ; return false ; int hungary() int res = 0 ,u; - 1 , sizeof (linker)); for (u = 1 ;u <= uN;u ++ ) 0 , sizeof (used)); if (dfs(u)) res ++ ; return res; int main() int K,x,y; int i,j; int ans; int iCase = 0 ; while (scanf( " %d%d%d " , & uN, & vN, & K) != EOF) ++ ; 0 , sizeof (g)); while (K -- ) " %d%d " , & x, & y); = 1 ; = hungary(); int cnt = 0 ; for (i = 1 ;i <= uN;i ++ ) for (j = 1 ;j <= vN;j ++ ) if (g[i][j] == 1 ) = 0 ; if (ans > hungary()) cnt ++ ; = 1 ; " Board %d have %d important blanks for %d chessmen.\n " ,iCase,cnt,ans); return 0 ;
Swap
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Special Judge
Problem Description
Given an N*N matrix with each entry equal to 0 or 1. You can swap any two rows or any two columns. Can you find a way to make all the diagonal entries equal to 1?
Input
There are several test cases in the input. The first line of each test case is an integer N (1 <= N <= 100). Then N lines follow, each contains N numbers (0 or 1), separating by space, indicating the N*N matrix.
Output
For each test case, the first line contain the number of swaps M. Then M lines follow, whose format is “R a b” or “C a b”, indicating swapping the row a and row b, or swapping the column a and column b. (1 <= a, b <= N). Any correct answer will be accepted, but M should be more than 1000.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
gaojie
#include < stdio.h > < string .h > const int MAXN = 105 ; int uN,vN; // u,v數目 int g[MAXN][MAXN]; // 編號是0~n-1的 int linker[MAXN]; bool used[MAXN]; int a[ 10000 ],b[ 10000 ]; bool dfs( int u) int v; for (v = 1 ;v <= vN;v ++ ) if (g[u][v] &&! used[v]) = true ; if (linker[v] ==- 1 || dfs(linker[v])) = u; return true ; return false ; int hungary() int res = 0 ; int u; - 1 , sizeof (linker)); for (u = 1 ;u <= uN;u ++ ) 0 , sizeof (used)); if (dfs(u)) res ++ ; return res; int main() int N; int i,j,u,v; while (scanf( " %d " , & N) != EOF) = vN = N; for (i = 1 ;i <= uN;i ++ ) for (j = 1 ;j <= vN;j ++ ) " %d " , & g[i][j]); int ans = hungary(); // printf("%d\n",ans); if (ans < N){printf( " -1\n " ); continue ;} int res = 0 ; for (i = 1 ;i <= uN;i ++ ) for (j = i;j <= vN;j ++ ) if (linker[j] == i) break ; if (j != i) = i;b[res ++ ] = j; int t = linker[i];linker[i] = linker[j];linker[j] = t; " %d\n " ,res); for (i = 0 ;i < res;i ++ ) " C %d %d\n " ,a[i],b[i]); return 0 ;
日 一 二 三 四 五 六 31 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
公告 導航
統計
隨筆: 100
文章: 0
評論: 2
引用: 0
常用鏈接
留言簿(2)
隨筆分類
隨筆檔案
博客
搜索
最新評論
閱讀排行榜
評論排行榜