How do we calculate the angle between two vectors?
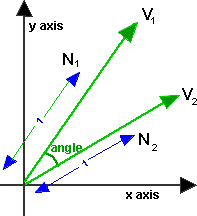
For 2D Vectors
This is relatively simple because there is only one degree of freedom for 2D rotations. If v1 and v2 are normalised so that |v1|=|v2|=1, then,
angle = acos(v1•v2)
where:
- • = 'dot' product (see box on right of page).
- acos = arc cos = inverse of cosine function see trigonometry page.
- |v1|= magnitude of v1.
The only problem is, this won't give all possible values between 0° and 360°, or -180° and +180°. In other words, it won't tell us if v1 is ahead or behind v2, to go from v1 to v2 is the opposite direction from v2 to v1.
In most math libraries acos will usually return a value between 0 and PI (in radians) which is 0° and 180°.
If we want a + or - value to indicate which vector is ahead, then we probably need to use the atan2 function (as explained on this page). using:
angle of 2 relative to 1= atan2(v2.y,v2.x) - atan2(v1.y,v1.x)
For 3D Vectors
Axis Angle Result
This is easiest to calculate using axis-angle representation because:
- the angle is given by acos of the dot product of the two (normalised) vectors: v1•v2 = |v1||v2| cos(angle)
- the axis is given by the cross product of the two vectors, the length of this axis is given by |v1 x v2| = |v1||v2| sin(angle).
as explained here
this is taken from this discussion.
So, if v1 and v2 are normalised so that |v1|=|v2|=1, then,
angle = acos(v1•v2)
axis = norm(v1 x v2)
If the vectors are parallel (angle = 0 or 180 degrees) then the length of v1 x v2 will be zero because sin(0)=sin(180)=0. In the zero case the axis does not matter and can be anything because there is no rotation round it. In the 180 degree case the axis can be anything at 90 degrees to the vectors so there is a whole range of possible axies.
| angle (degrees) |
sin(angle) |
cos(angle) |
v1•v2 |
v1 x v2 |
| 0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0,0,0 |
| 90 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
unit len |
| 180 |
0 |
-1 |
-1 |
0,0,0 |
| 270 |
-1 |
0 |
0 |
unit len |
Quaternion Result
One approach might be to define a quaternion which, when multiplied by a vector, rotates it:
p2=q * p1
This almost works as explained on this page.
However, to rotate a vector, we must use this formula:
p2=q * p1 * conj(q)
where:
- p2 = is a vector representing a point after being rotated
- q = is a quaternion representing a rotation.
- p1= is a vector representing a point before being rotated
This is a bit messy to solve for q, I am therefore grateful to minorlogic for the following approach which converts the axis angle result to a quaternion:
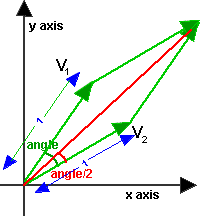
The axis angle can be converted to a quaternion as follows, let x,y,z,w be elements of quaternion, these can be expressed in terms of axis angle as explained here.
angle = arcos(v1•v2/ |v1||v2|)
axis = norm(v1 x v2)
s = sin(angle/2)
x = axis.x *s
y = axis.y *s
z = axis.z *s
w = cos(angle/2)
We can use this half angle trig formula on this page: sin(angle/2) = 0.5 sin(angle) / cos(angle/2)
so substituting in quaternion formula gives:
s = 0.5 sin(angle) / cos(angle/2)
x = norm(v1 x v2).x *s
y = norm(v1 x v2).y *s
z = norm(v1 x v2).z *s
w = cos(angle/2)
multiply x,y,z and w by 2* cos(angle/2) (this will de normalise the quaternion but we can always normalise later)
x = norm(v1 x v2).x * sin(angle)
y = norm(v1 x v2).y * sin(angle)
z = norm(v1 x v2).z * sin(angle)
w = 2 * cos(angle/2) * cos(angle/2)
now substitute half angle trig formula on this page: cos(angle/2) = sqrt(0.5*(1 + cos (angle)))
x = norm(v1 x v2).x * sin(angle)
y = norm(v1 x v2).y * sin(angle)
z = norm(v1 x v2).z * sin(angle)
w = 1 + cos (angle)
because |v1 x v2| = |v1||v2| sin(angle) we can normalise (v1 x v2) by dividing it with sin(angle),
also apply v1•v2 = |v1||v2| cos(angle)so,
x = (v1 x v2).x / |v1||v2|
y = (v1 x v2).y/ |v1||v2|
z = (v1 x v2).z/ |v1||v2|
w = 1 + v1•v2 / |v1||v2|
If v1 and v2 are already normalised then |v1||v2|=1 so,
x = (v1 x v2).x
y = (v1 x v2).y
z = (v1 x v2).z
w = 1 + v1•v2
If v1 and v2 are not already normalised then multiply by |v1||v2| gives:
x = (v1 x v2).x
y = (v1 x v2).y
z = (v1 x v2).z
w = |v1||v2| + v1•v2