epoll Scalability Web Page
Introduction
Davide Libenzi wrote an event poll implementation and described it at the /dev/epoll home page here. His performance testing led to the conclusion that epoll scaled linearly regardless of the load as defined by the number of dead connections. However, the main hindrance to having epoll accepted into the mainline Linux kernel by Linus Torvalds was the interface to epoll being in /dev. Therefore, a new interface to epoll was added via three new system calls. That interface will hereafter be referred to as sys_epoll. Download sys_epoll here.
sys_epoll Interface
-
int epoll_create(int maxfds);
The system call epoll_create() creates a sys_epoll "object" by allocating space for "maxfds" descriptors to be polled. The sys_epoll "object" is referenced by a file descriptor, and this enables the new interface to :
- Maintain compatibility with the existing interface
- Avoid the creation of a epoll_close() syscall
- Reuse 95% of the existing code
- Inherit the file* automatic clean up code
-
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, unsigned int events);
The system call epoll_ctl() is the controller interface. The "op" parameter is either EP_CTL_ADD, EP_CTL_DEL or EP_CTL_MOD. The parameter "fd" is the target of the operation. The last parameter, "events", is used in both EP_CTL_ADD and EP_CTL_MOD and represents the event interest mask.
-
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct pollfd * events, int maxevents, int timeout);
The system call epoll_wait() waits for events by allowing a maximum timeout, "timeout", in milliseconds and returns the number of events ( struct pollfd ) that the caller will find available at "*events".
sys_epoll Man Pages
Testing
We tested using two applications:
dphttpd
Software
The http client is httperf from David Mosberger. Download httperf here. The http server is dphttpd from Davide Libenzi. Download dphttpd here. The deadconn client is also provided by Davide Libenzi. Download deadconn here.
Two client programs (deadconn_last and httperf) run on the client machine and establish connections to the HTTP server (dphttpd) running on the server machine. Connections established by deadconn_last are "dead". These send a single HTTP get request at connection setup and remain idle for the remainder of the test. Connections established by httperf are "active". These continuously send HTTP requests to the server at a fixed rate. httperf reports the rate at which the HTTP server replies to its requests. This reply rate is the metric reported on the Y-axis of the graphs below.
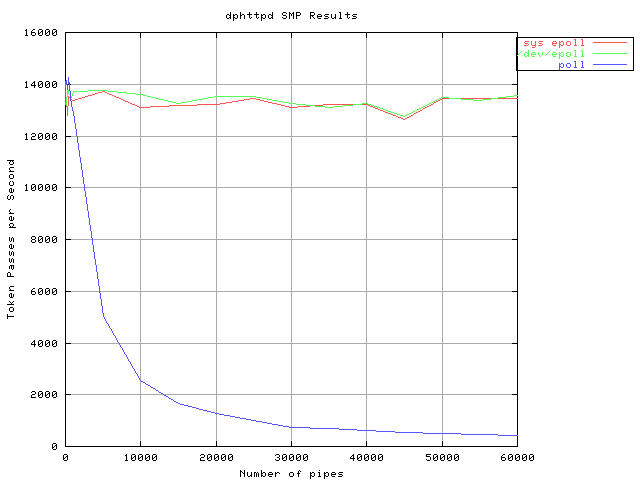
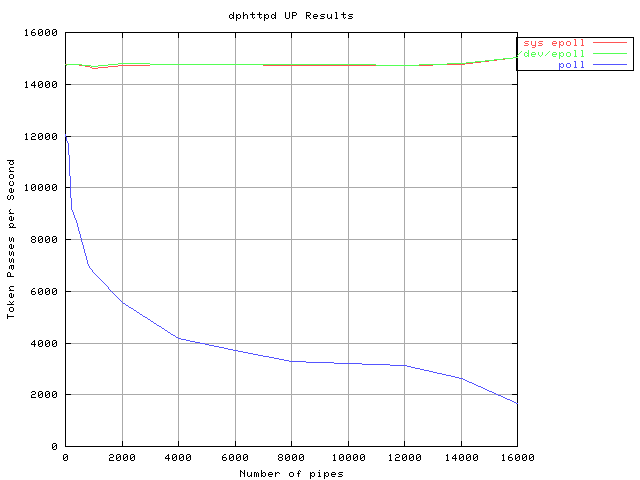
For the tests, the number of active connections is kept constant and the number of dead connections increased from 0 to 60000 (X-axis of graphs below). Consequently, dphttpd spends a fixed amount of time responding to requests and a variable amount of time looking for requests to service. The mechanism used to look for active connections amongst all open connections is one of standard poll(), /dev/epoll or sys_epoll. As the number of dead connections is increased, the scalability of these mechanisms starts impacting dphttpd's reply rate, measured by httperf.
dphttpd SMP
Server
- Hardware: 8-way PIII Xeon 700MHz, 2.5 GB RAM, 2048 KB L2 cache
- OS : RedHat 7.3 with 2.5.44 kernel, patched with ONE of:
- /proc/sys/fs/file-max = 131072
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_fin_timeout = 15
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_tw_reuse = 1
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_tw_recycle = 1
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range = 1024 65535
- # ulimit -n 131072
- # dphttpd --maxfds 20000 --stksize 4096
- default size of reply = 128 bytes
Client
- Hardware: 4-way PIII Xeon 500MHz, 3 GB RAM, 512 KB L2 cache
- OS : RedHat 7.3 with 2.4.18-3smp kernel
- /proc/sys/fs/file-max = 131072
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_fin_timeout = 15
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65535
- # ulimit -n 131072
- # deadconn_last $SERVER $SVRPORT num_connections
where num_connections is one of 0, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800, 1000, 5000, 10000, 15000, 20000, 25000, 30000, 35000, 40000, 45000, 50000, 55000, 60000.
- After deadconn_last reports num_connections established
# httperf --server=$SERVER --port=$SVRPORT --think-timeout 5 --timeout 5 --num-calls 20000 --num-conns 100 --hog --rate 100
Results for dphttpd SMP
dphttpd UP
Server
- 1-way PIII, 866MHz, 256 MB RAM
- OS: 2.5.44 gcc 2.96 (RedHat 7.3)
- /proc/sys/fs/file-max = 65536
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_fin_timeout = 15
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_tw_recycle = 1
- # ulimit -n 65536
- # dphttpd --maxfds 20000 --stksize 4096
- default size of reply = 128 bytes
Client
- 1-way PIII, 866MHz, 256 MB RAM
- OS: 2.4.18, gcc 2.96 (RedHat 7.3)
- /proc/sys/fs/file-max = 65536
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_fin_timeout = 15
- /proc/sys/net/ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
- # ulimit -n 65536
- # deadconn_last $SERVER $SVRPORT num_connections
where num_connections is one of 0, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800, 1000, 2000, 4000, 6000, 8000, 10000, 12000, 14000, 16000.
- After deadconn_last reports num_connections established
# httperf --server=$SERVER --port=$SVRPORT --think-timeout 5 --timeout 5 --num-calls 20000 --num-conns 100 --hog --rate 100
Results for dphttpd UP
Pipetest
David Stevens added support for sys_epoll to Ben LaHaise's original pipetest.c application. Download Ben LaHaise's Ottawa Linux Symposium 2002 paper including pipetest.c here.Download David Steven's patch to add sys_epoll to pipetest.c here.
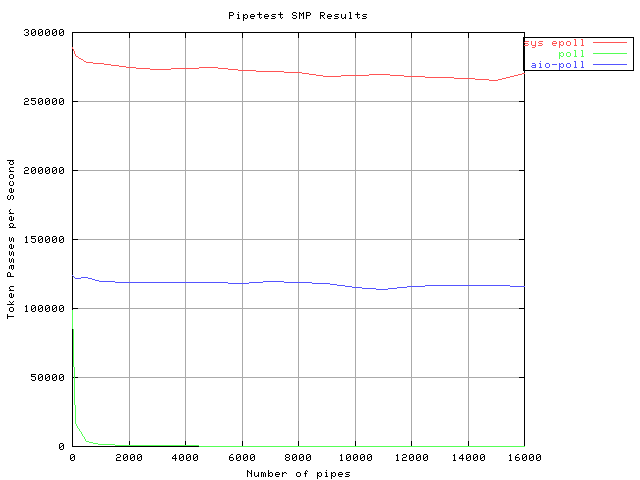
Pipetest SMP
System and Configuration
- 8-way PIII Xeon 900MHz, 4 GB RAM, 2048 KB L2 cache
- OS: RedHat 7.2 with 2.5.44 kernel, patched with one of:
- /proc/sys/fs/file-max = 65536
- # ulimit -n 65536
- # pipetest [poll|aio-poll|sys-epoll] num_pipes message_threads max_generation
- where num_pipes is one of 10, 100, 500, or 1000-16000 in increments of 1000
- message_threads is 1
- max_generantion is 300
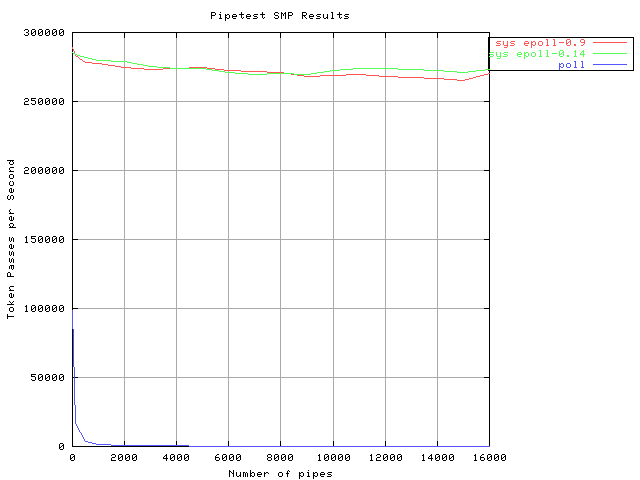
Results for pipetest on an SMP
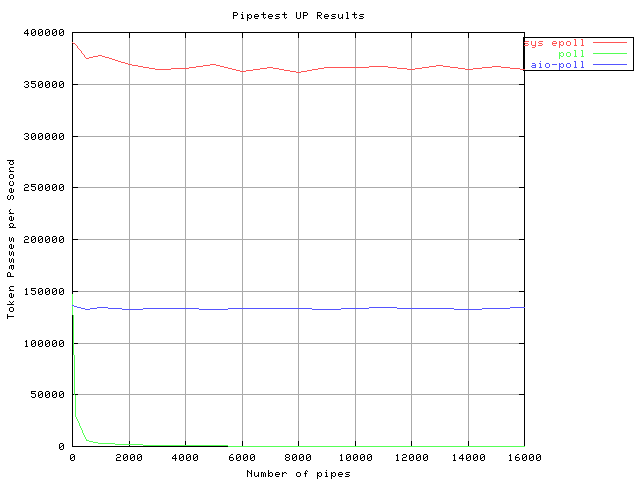
Results for Pipetest on a UP
Same Hardware and Configuration as with the SMP pipetest above
with CONFIG_SMP = n being the only change.
sys_epoll stability comparisons Oct 30, 2002
Following are performance results comparing version 0.14 of the (Download v0.14 here) to the version, v0.9, originally used for the performance testing outlined above. (Download v0.9 here) Testing was done using two measures: pipetest details here. and dphttpd details here..

Analysis and Conclusion
The system call interface to epoll performs as well as the /dev interface to epoll. In addition sys_epoll scales better than poll and AIO poll for large numbers of connections. Other points in favour of sys_epoll are:
Due to these factors sys_epoll should be seriously considered for inclusion in the mainline Linux kernel.
Acknowledgments
Thank You to: Davide Libenzi Who wrote /dev/epoll, sys_epoll and dphttpd.
He was an all around great guy to work with.
Also Thanks to the following people who helped with testing and this web site:
Shailabh Nagar, Paul Larson , Hanna Linder, and David Stevens.