Supermarket
Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:65536K
Total Submit:987 Accepted:369
Description
A supermarket has a set Prod of products on sale. It earns a profit px for each product x∈Prod sold by a deadline dx that is measured as an integral number of time units starting from the moment the sale begins. Each product takes precisely one unit of time for being sold. A selling schedule is an ordered subset of products Sell ≤ Prod such that the selling of each product x∈Sell, according to the ordering of Sell, completes before the deadline dx or just when dx expires. The profit of the selling schedule is Profit(Sell)=Σx∈Sellpx. An optimal selling schedule is a schedule with a maximum profit.
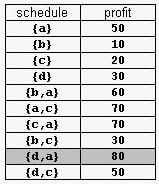
For example, consider the products Prod={a,b,c,d} with (pa,da)=(50,2), (pb,db)=(10,1), (pc,dc)=(20,2), and (pd,dd)=(30,1). The possible selling schedules are listed in table 1. For instance, the schedule Sell={d,a} shows that the selling of product d starts at time 0 and ends at time 1, while the selling of product a starts at time 1 and ends at time 2. Each of these products is sold by its deadline. Sell is the optimal schedule and its profit is 80.
Write a program that reads sets of products from an input text file and computes the profit of an optimal selling schedule for each set of products.
Input
A set of products starts with an integer 0 <= n <= 10000, which is the number of products in the set, and continues with n pairs pi di of integers, 1 <= pi <= 10000 and 1 <= di <= 10000, that designate the profit and the selling deadline of the i-th product. White spaces can occur freely in input. Input data terminate with an end of file and are guaranteed correct.
Output
For each set of products, the program prints on the standard output the profit of an optimal selling schedule for the set. Each result is printed from the beginning of a separate line.
Sample Input
4 50 2 10 1 20 2 30 1
7 20 1 2 1 10 3 100 2 8 2
5 20 50 10
Sample Output
80
185
Hint
The sample input contains two product sets. The first set encodes the products from table 1. The second set is for 7 products. The profit of an optimal schedule for these products is 185.
Source
Southeastern Europe 2003
貪心是很容易想到的 盡可能將利潤大的選中 然后盡可能放到DeadLine附近去
這里就有一個問題 怎樣盡快拿到一個deadLine往上數第一個空閑日期?
想法0:直接搜o(n^2)的查找總費時 可能超時!
想法1:線段樹!問題建模:一個數的前面第幾個是空閑?
對10000的區間建立線段樹 可以將查詢復雜度降低到NlogN
想法2: 并查集!對一個連續非空閑區間建立集合 其代表元選擇上面第一個空閑的日期!時間復雜度再降低到o(N)! 系數為ackman函數 很小
Problem Id:1456 User Id:oyjpart
Memory:172K Time:15MS
Language:G++ Result:Accepted
//by oyjpArt
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int ng;
struct good{int p, d;}g[N];
int p[N];
bool flag[N];
bool operator < (const good& a, const good& b) {return a.p > b.p; }
int find_set(int a) {
int t = a;
while(t != p[t]) t = p[t];
int r = a;
while(r != p[r]) { int k = p[r]; p[r] = t; r = k; }
return t;
}
int main() {
int i;
while(scanf("%d", &ng) != EOF) {
memset(flag, 0, sizeof(flag));
int maxd = 0;
for(i = 0; i<ng; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &(g[i].p), &(g[i].d));
if(g[i].d > maxd) maxd = g[i].d;
}
for(i = 1; i<maxd; i++)
p[i] = i;
sort(g, g+ng);
int cnt = 0;
for(i = 0; i<ng; i++) {
int d;
if(!flag[g[i].d]) { d = g[i].d; p[d] = d-1; }
else d = find_set(g[i].d);
if(d > 0) cnt += g[i].p;
flag[d] = 1;
if(d > 0 && flag[d+1]) p[d] = p[d-1];
}
printf("%d\n", cnt);
}
return 0;
}