Description
Node 3 is therefore a Single Point of Failure (SPF) for this network. Strictly, an SPF will be defined as any node that, if unavailable, would prevent at least one pair of available nodes from being able to communicate on what was previously a fully connected network. Note that the network on the right has no such node; there is no SPF in the network. At least two machines must fail before there are any pairs of available nodes which cannot communicate.
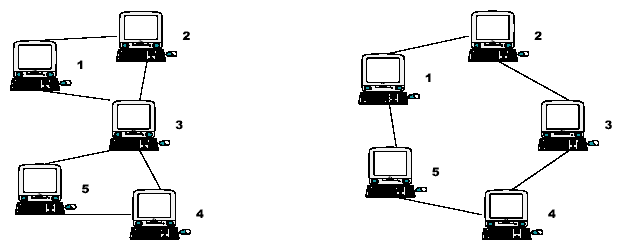
Input
Output
The first network in the file should be identified as "Network #1", the second as "Network #2", etc. For each SPF node, output a line, formatted as shown in the examples below, that identifies the node and the number of fully connected subnets that remain when that node fails. If the network has no SPF nodes, simply output the text "No SPF nodes" instead of a list of SPF nodes.
Sample Input
1 2 5 4 3 1 3 2 3 4 3 5 0 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 1 0 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 6 6 3 2 5 5 1 0 0
Sample Output
Network #1 SPF node 3 leaves 2 subnets Network #2 No SPF nodes Network #3 SPF node 2 leaves 2 subnets SPF node 3 leaves 2 subnets
дәҢгҖҒеҲҶжһ?br> з”ЁDFSи§ЈеҶій—®йўҳеQҢиҜҰҫlҶз®—жі•пјҡ(xЁ¬)еүІзӮ№дёҺжЎҘгҖ?/span>
дёүгҖҒд»Јз ?br>
 #include<iostream>
#include<iostream>2
 #include<list>
#include<list>3
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;4
 int t;
int t;5
 int v1, v2;
int v1, v2;6
 list<int> g[1001];
list<int> g[1001];7
 bool flag;
bool flag;8
 int root;
int root;9
 int counter;
int counter;10
 bool spf[1001];
bool spf[1001];11
 int low[1001], lab[1001];
int low[1001], lab[1001];12
 bool visit[1001];
bool visit[1001];13
 void dfs(int u, int fa)
void dfs(int u, int fa)14


 {
{15
 low[u] = lab[u] = counter++;
low[u] = lab[u] = counter++;16
 list<int>::iterator it;
list<int>::iterator it;17
 int counter = 0;
int counter = 0;18
 for(it = g[u].begin(); it != g[u].end(); it++)
for(it = g[u].begin(); it != g[u].end(); it++)19


 {
{20
 int v = *it;
int v = *it;21
 if(!lab[v])
if(!lab[v])22


 {
{23
 counter++;
counter++;24
 dfs(v, u);
dfs(v, u);25
 low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);26
 if((u==root && counter>=2) || (u!=root && low[v]>=lab[u]))
if((u==root && counter>=2) || (u!=root && low[v]>=lab[u]))27
 spf[u] = flag = true;
spf[u] = flag = true;28
 }
}29
 else if(v != fa)
else if(v != fa)30
 low[u] = min(low[u], lab[v]);
low[u] = min(low[u], lab[v]);31
 }
}32
 }
}33
 void find(int u)
void find(int u)34


 {
{35
 visit[u] = true;
visit[u] = true;36
 list<int>::iterator it;
list<int>::iterator it;37
 for(it = g[u].begin(); it != g[u].end(); it++)
for(it = g[u].begin(); it != g[u].end(); it++)38
 if(!visit[*it])
if(!visit[*it])39
 find(*it);
find(*it);40
 }
}41
 int main()
int main()42


 {
{43
 t = 1;
t = 1;44
 while(1)
while(1)45


 {
{46
 scanf("%d", &v1);
scanf("%d", &v1);47
 if(v1 == 0) break;
if(v1 == 0) break;48
 for(int i=1; i<=1000; i++)
for(int i=1; i<=1000; i++)49
 g[i].clear();
g[i].clear();50
 memset(spf, 0, sizeof spf);
memset(spf, 0, sizeof spf);51
 memset(low, 0, sizeof low);
memset(low, 0, sizeof low);52
 memset(lab, 0, sizeof lab);
memset(lab, 0, sizeof lab);53
 while(v1 != 0)
while(v1 != 0)54


 {
{55
 scanf("%d", &v2);
scanf("%d", &v2);56
 g[v1].push_back(v2);
g[v1].push_back(v2);57
 g[v2].push_back(v1);
g[v2].push_back(v1);58
 root = v1;
root = v1;59
 scanf("%d", &v1);
scanf("%d", &v1);60
 }
}61
 counter = 1;
counter = 1;62
 flag = false;
flag = false;63
 dfs(root, -1);
dfs(root, -1);64
 printf("Network #%d\n", t++);
printf("Network #%d\n", t++);65
 if(flag)
if(flag)66


 {
{67
 for(int i=1; i<=1000; i++)
for(int i=1; i<=1000; i++)68


 {
{69
 if(!spf[i]) continue;
if(!spf[i]) continue;70
 int cnt = 0;
int cnt = 0;71
 memset(visit, 0, sizeof visit);
memset(visit, 0, sizeof visit);72
 visit[i] = true;
visit[i] = true;73
 list<int>::iterator it;
list<int>::iterator it;74
 for(it = g[i].begin(); it != g[i].end(); it++)
for(it = g[i].begin(); it != g[i].end(); it++)75
 if(!visit[*it])
if(!visit[*it])76


 {
{77
 cnt++;
cnt++;78
 find(*it);
find(*it);79
 }
}80
 printf(" SPF node %d leaves %d subnets\n", i, cnt);
printf(" SPF node %d leaves %d subnets\n", i, cnt);81
 }
}82
 }
}83
 else
else84
 printf(" No SPF nodes\n");
printf(" No SPF nodes\n");85
 printf("\n");
printf("\n");86
 }
}87
 }
}
For each test case,in the first line there are two numbers n(2<=n<=40000) and m (1<=m<=200),the number of houses and the number of queries. The following n-1 lines each consisting three numbers i,j,k, separated bu a single space, meaning that there is a road connecting house i and house j,with length k(0<k<=40000).The houses are labeled from 1 to n.
Next m lines each has distinct integers i and j, you areato answer the distance between house i and house j.
2 3 2 1 2 10 3 1 15 1 2 2 3 2 2 1 2 100 1 2 2 1
10 25 100 100
дәҢгҖҒеҲҶжһ?br> з”ЁTarjanи§ЈеҶізҡ„LCAй—®йўҳеQҢиҜҰҫlҶз®—жі•пјҡ(xЁ¬)LCAй—®йўҳгҖ?/span>
дёүгҖҒд»Јз ?/p>
 #include<iostream>
#include<iostream>
2 #include<list>
#include<list>
3 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
4 struct node
struct node
5

 {
{
6 int v, d;
int v, d;
7
 void init(int vv, int dd)
void init(int vv, int dd)  {v = vv; d = dd;};
{v = vv; d = dd;};
8 };
};
9 int t, n, m, v1, v2, len;
int t, n, m, v1, v2, len;
10 list<node> g[40001];
list<node> g[40001];
11 list<node> query[40001];
list<node> query[40001];
12 int dis[40001];
int dis[40001];
13 int res[201][3];
int res[201][3];
14 int parent[40001];
int parent[40001];
15 bool visit[40001];
bool visit[40001];
16 int find(int k)
int find(int k)
17

 {
{
18 if(parent[k] == k)
if(parent[k] == k)
19 return k;
return k;
20 return parent[k] = find(parent[k]);
return parent[k] = find(parent[k]);
21 }
}
22 void tarjan(int u)
void tarjan(int u)
23

 {
{
24 if(visit[u]) return;
if(visit[u]) return;
25 visit[u] = true;
visit[u] = true;
26 parent[u] = u;
parent[u] = u;
27 list<node>::iterator it = query[u].begin();
list<node>::iterator it = query[u].begin();
28 while(it != query[u].end())
while(it != query[u].end())
29

 {
{
30 if(visit[it->v])
if(visit[it->v])
31 res[it->d][2] = find(it->v);
res[it->d][2] = find(it->v);
32 it++;
it++;
33 }
}
34 it = g[u].begin();
it = g[u].begin();
35 while(it != g[u].end())
while(it != g[u].end())
36

 {
{
37 if(!visit[it->v])
if(!visit[it->v])
38

 {
{
39 dis[it->v] = min(dis[it->v], dis[u] + it->d);
dis[it->v] = min(dis[it->v], dis[u] + it->d);
40 tarjan(it->v);
tarjan(it->v);
41 parent[it->v] = u;
parent[it->v] = u;
42 }
}
43 it++;
it++;
44 }
}
45 }
}
46 int main()
int main()
47

 {
{
48 scanf("%d", &t);
scanf("%d", &t);
49 while(t--)
while(t--)
50

 {
{
51 scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
52 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
53 g[i].clear();
g[i].clear();
54 for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
55 query[i].clear();
query[i].clear();
56 for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
57

 {
{
58 scanf("%d%d%d", &v1, &v2, &len);
scanf("%d%d%d", &v1, &v2, &len);
59 node n1; n1.init(v2, len);
node n1; n1.init(v2, len);
60 g[v1].push_back(n1);
g[v1].push_back(n1);
61 node n2; n2.init(v1, len);
node n2; n2.init(v1, len);
62 g[v2].push_back(n2);
g[v2].push_back(n2);
63 }
}
64 for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
65

 {
{
66 scanf("%d%d", &v1, &v2);
scanf("%d%d", &v1, &v2);
67 res[i][0] = v1;
res[i][0] = v1;
68 res[i][1] = v2;
res[i][1] = v2;
69 node n1; n1.init(v2, i);
node n1; n1.init(v2, i);
70 query[v1].push_back(n1);
query[v1].push_back(n1);
71 node n2; n2.init(v1, i);
node n2; n2.init(v1, i);
72 query[v2].push_back(n2);
query[v2].push_back(n2);
73 }
}
74 memset(visit, 0, sizeof(visit));
memset(visit, 0, sizeof(visit));
75 memset(dis, 0x7f, sizeof(dis));
memset(dis, 0x7f, sizeof(dis));
76 dis[1] = 0;
dis[1] = 0;
77 tarjan(1);
tarjan(1);
78 for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
79 printf("%d\n", dis[res[i][0]] + dis[res[i][1]] - 2*dis[res[i][2]]);
printf("%d\n", dis[res[i][0]] + dis[res[i][1]] - 2*dis[res[i][2]]);
80 }
}
81 }
}
Description

An example is in figure 1. The label x/y of power station u shows that p(u)=x and pmax(u)=y. The label x/y of consumer u shows that c(u)=x and cmax(u)=y. The label x/y of power transport line (u,v) shows that l(u,v)=x and lmax(u,v)=y. The power consumed is Con=6. Notice that there are other possible states of the network but the value of Con cannot exceed 6.
Input
Output
Sample Input
2 1 1 2 (0,1)20 (1,0)10 (0)15 (1)20 7 2 3 13 (0,0)1 (0,1)2 (0,2)5 (1,0)1 (1,2)8 (2,3)1 (2,4)7 (3,5)2 (3,6)5 (4,2)7 (4,3)5 (4,5)1 (6,0)5 (0)5 (1)2 (3)2 (4)1 (5)4
Sample Output
15 6
дәҢгҖҒеҲҶжһ?br> еўһеҠ зӮ№nдёәsеQҢзӮ№n+1дёәtеQҢжұӮжңҖеӨ§жөҒеQҢдӢЙз”ЁPush-RelabelҪҺ—жі•еQҢе…·дҪ“з®—жі•пјҡ(xЁ¬)жңҖеӨ§жөҒй—®йўҳ
дёүгҖҒд»Јз ?/strong>
 #include<iostream>
#include<iostream>2
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;3
 #define MAXN 202
#define MAXN 2024
 int s, t;
int s, t;5
 int n, np, nc, m;
int n, np, nc, m;6
 char str[50];
char str[50];7
 int c[MAXN][MAXN];
int c[MAXN][MAXN];8
 int f[MAXN][MAXN];
int f[MAXN][MAXN];9
 int e[MAXN];
int e[MAXN];10
 int h[MAXN];
int h[MAXN];11
 void push(int u, int v)
void push(int u, int v)12


 {
{13
 int d = min(e[u], c[u][v] - f[u][v]);
int d = min(e[u], c[u][v] - f[u][v]);14
 f[u][v] += d;
f[u][v] += d;15
 f[v][u] = -f[u][v];
f[v][u] = -f[u][v];16
 e[u] -= d;
e[u] -= d;17
 e[v] += d;
e[v] += d;18
 }
}19
 bool relabel(int u)
bool relabel(int u)20


 {
{21
 int mh = INT_MAX;
int mh = INT_MAX;22
 for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++)
for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++)23


 {
{24
 if(c[u][i] > f[u][i])
if(c[u][i] > f[u][i])25
 mh = min(mh, h[i]);
mh = min(mh, h[i]);26
 }
}27
 if(mh == INT_MAX)
if(mh == INT_MAX)28
 return false; //ҢDӢз•ҷҫ|‘з»ңдёӯж— д»ҺuеҮәеҸ‘зҡ„иө\
return false; //ҢDӢз•ҷҫ|‘з»ңдёӯж— д»ҺuеҮәеҸ‘зҡ„иө\29
 h[u] = mh + 1;
h[u] = mh + 1;30
 for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++)
for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++)31


 {
{32
 if(e[u] == 0) //е·Іж— дҪҷжөҒеQҢдёҚйңҖеҶҚж¬Ўpush
if(e[u] == 0) //е·Іж— дҪҷжөҒеQҢдёҚйңҖеҶҚж¬Ўpush33
 break;
break;34
 if(h[i] == mh && c[u][i] > f[u][i]) //pushзҡ„жқЎд»?/span>
if(h[i] == mh && c[u][i] > f[u][i]) //pushзҡ„жқЎд»?/span>35
 push(u, i);
push(u, i);36
 }
}37
 return true;
return true;38
 }
}39
 void init_preflow()
void init_preflow()40


 {
{41
 memset(h, 0, sizeof(h));
memset(h, 0, sizeof(h));42
 memset(e, 0, sizeof(e));
memset(e, 0, sizeof(e));43
 h[s] = n+2;
h[s] = n+2;44
 for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++)
for(int i=0; i<n+2; i++)45


 {
{46
 if(c[s][i] == 0)
if(c[s][i] == 0)47
 continue;
continue;48
 f[s][i] = c[s][i];
f[s][i] = c[s][i];49
 f[i][s] = -f[s][i];
f[i][s] = -f[s][i];50
 e[i] = c[s][i];
e[i] = c[s][i];51
 e[s] -= c[s][i];
e[s] -= c[s][i];52
 }
}53
 }
}54
 void push_relabel()
void push_relabel()55


 {
{56
 init_preflow();
init_preflow();57
 bool flag = true; //иЎЁзӨәжҳҜеҗҰҳqҳжңүrelabelж“ҚдҪң
bool flag = true; //иЎЁзӨәжҳҜеҗҰҳqҳжңүrelabelж“ҚдҪң58
 while(flag)
while(flag)59


 {
{60
 flag = false;
flag = false;61
 for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)62
 if(e[i] > 0)
if(e[i] > 0)63
 flag = flag || relabel(i);
flag = flag || relabel(i);64
 }
}65
 }
}66
 int main()
int main()67


 {
{68
 while(scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &np, &nc, &m) != EOF)
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &np, &nc, &m) != EOF)69


 {
{70
 s = n; t = n+1;
s = n; t = n+1;71
 memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));72
 memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));73
 while(m--)
while(m--)74


 {
{75
 scanf("%s", &str);
scanf("%s", &str);76
 int u=0, v=0, z=0;
int u=0, v=0, z=0;77
 sscanf(str, "(%d,%d)%d", &u, &v, &z);
sscanf(str, "(%d,%d)%d", &u, &v, &z);78
 c[u][v] = z;
c[u][v] = z;79
 }
}80
 for(int i=0; i<np+nc; i++)
for(int i=0; i<np+nc; i++)81


 {
{82
 scanf("%s", &str);
scanf("%s", &str);83
 int u=0, z=0;
int u=0, z=0;84
 sscanf(str, "(%d)%d", &u, &z);
sscanf(str, "(%d)%d", &u, &z);85
 if(i < np)
if(i < np)86
 c[s][u] = z;
c[s][u] = z;87
 else if(i >= np && i < np + nc)
else if(i >= np && i < np + nc)88
 c[u][t] = z;
c[u][t] = z;89
 }
}90
 push_relabel();
push_relabel();91
 printf("%d\n", e[t]);
printf("%d\n", e[t]);92
 }
}93
 }
}Description
Farmer John knows not only how many gallons of water each ditch can transport per minute but also the exact layout of the ditches, which feed out of the pond and into each other and stream in a potentially complex network.
Given all this information, determine the maximum rate at which water can be transported out of the pond and into the stream. For any given ditch, water flows in only one direction, but there might be a way that water can flow in a circle.
Input
Output
Sample Input
5 4 1 2 40 1 4 20 2 4 20 2 3 30 3 4 10
Sample Output
50
дәҢгҖҒеҲҶжһ?br> е…¶е®һһ®ұжҳҜд»ҘзӮ№1дёәsеQҢд»ҘзӮ№mдёәtеQҢжұӮжңҖеӨ§жөҒеQҢдҪҶжҳҜиҰҒжіЁж„Ҹиҫ“е…Ҙзҡ„иө\еҫ„еҸҜд»ҘйҮҚеӨ?и§Ғд»Јз ?0иЎ?еQҢдӢЙз”ЁEdmonds-KarpҪҺ—жі•еQҢе…·дҪ“з®—жі•пјҡ(xЁ¬)жңҖеӨ§жөҒй—®йўҳ
дёүгҖҒд»Јз ?br>
 #include<iostream>
#include<iostream>2
 #include<queue>
#include<queue>3
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;4
 #define MAXM 201
#define MAXM 2015
 int m, n;
int m, n;6
 int si, ei, ci;
int si, ei, ci;7
 int c[MAXM][MAXM];
int c[MAXM][MAXM];8
 int f[MAXM][MAXM];
int f[MAXM][MAXM];9
 int cf[MAXM][MAXM];
int cf[MAXM][MAXM];10
 bool visit[MAXM];
bool visit[MAXM];11
 int p[MAXM];
int p[MAXM];12
 struct node
struct node13


 {
{14
 int v, cf;
int v, cf;15
 void set(int vv, int ccf)
void set(int vv, int ccf)16


 {
{17
 v = vv; cf = ccf;
v = vv; cf = ccf;18
 }
}19
 };
};20
 int main()
int main()21


 {
{22
 while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF)
while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF)23


 {
{24
 memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));25
 memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));26
 memset(cf, 0, sizeof(cf));
memset(cf, 0, sizeof(cf));27
 while(n--)
while(n--)28


 {
{29
 scanf("%d%d%d", &si, &ei, &ci);
scanf("%d%d%d", &si, &ei, &ci);30
 c[si][ei] += ci;
c[si][ei] += ci;31
 cf[si][ei] = c[si][ei];
cf[si][ei] = c[si][ei];32
 }
}33
 bool flag = true; //з”ЁдәҺиЎЁзӨәжҳҜеҗҰжү‘ЦҲ°еўһе№ҝи·?/span>
bool flag = true; //з”ЁдәҺиЎЁзӨәжҳҜеҗҰжү‘ЦҲ°еўһе№ҝи·?/span>34
 while(flag)
while(flag)35


 {
{36
 flag = false;
flag = false;37
 memset(visit, 0, sizeof(visit));
memset(visit, 0, sizeof(visit));38
 queue<node> q;
queue<node> q;39
 node temp;
node temp;40
 temp.set(1, INT_MAX);
temp.set(1, INT_MAX);41
 p[1] = 0;
p[1] = 0;42
 q.push(temp); visit[1] = true;
q.push(temp); visit[1] = true;43
 while(!q.empty()) //тqҝеәҰдјҳе…ҲжҗңзғҰ(chЁі)
while(!q.empty()) //тqҝеәҰдјҳе…ҲжҗңзғҰ(chЁі)44


 {
{45
 node temp = q.front(); q.pop();
node temp = q.front(); q.pop();46
 for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)47


 {
{48
 if(temp.v == i || visit[i] || cf[temp.v][i] == 0)
if(temp.v == i || visit[i] || cf[temp.v][i] == 0)49
 continue;
continue;50
 node newNode;
node newNode; 51
 newNode.set(i, min(temp.cf, cf[temp.v][i]));
newNode.set(i, min(temp.cf, cf[temp.v][i]));52
 p[i] = temp.v;
p[i] = temp.v;53
 q.push(newNode);
q.push(newNode);54
 visit[i] = true;
visit[i] = true;55
 if(i == m)
if(i == m)56


 {
{57
 flag = true; //жү‘ЦҲ°еўһе№ҝи·?/span>
flag = true; //жү‘ЦҲ°еўһе№ҝи·?/span>58
 break;
break;59
 }
}60
 }
}61
 if(flag)
if(flag)62
 break;
break;63
 }
}64
 if(flag)
if(flag)65


 {
{66
 int mincf = q.back().cf;
int mincf = q.back().cf;67
 int v1 = p[m], v2 = m;
int v1 = p[m], v2 = m;68
 while(v1 != 0)
while(v1 != 0)69


 {
{70
 f[v1][v2] += mincf; //дҝ®ж”№Ӣ№?/span>
f[v1][v2] += mincf; //дҝ®ж”№Ӣ№?/span>71
 f[v2][v1] = -f[v1][v2];
f[v2][v1] = -f[v1][v2];72
 cf[v1][v2] = c[v1][v2] - f[v1][v2]; //дҝ®ж”№ҢDӢз•ҷе®ҡwҮҸ
cf[v1][v2] = c[v1][v2] - f[v1][v2]; //дҝ®ж”№ҢDӢз•ҷе®ҡwҮҸ73
 cf[v2][v1] = c[v2][v1] - f[v2][v1];
cf[v2][v1] = c[v2][v1] - f[v2][v1];74
 v2 = v1;
v2 = v1;75
 v1 = p[v1];
v1 = p[v1];76
 }
}77
 }
}78
 }
}79
 int res = 0;
int res = 0;80
 for(int i=2; i<=m; i++) //и®Ўз®—жңҖеӨ§жөҒ
for(int i=2; i<=m; i++) //и®Ўз®—жңҖеӨ§жөҒ81
 res += f[1][i];
res += f[1][i];82
 printf("%d\n", res);
printf("%d\n", res);83
 }
}84
 }
}