Description
Input
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For example, for the following tree:
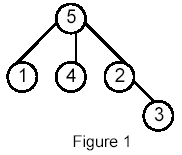
Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1
5:5
йўҳж„ҸеQҡз»ҷеҮәж ‘зҡ„з»“жһ„пјҢеҶҚз»ҷеҮшҷҰҒиҜўй—®зҡ„пјҲuеQ?v),жұӮеҮәиҜўй—®еҗҺе…¬е…ЮpҠӮзӮ№еҮәзҺ°зҡ„дёӘж•°гҖ?br>д»Јз ҒеQ?br>#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#define maxn 1000
using namespace std;
int visit[maxn], in[maxn], f[maxn], anc[maxn], num[maxn];
vector<int> tree[maxn], que[maxn];
void set(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
in[i] = 0;
visit[i] = 0;
num[i] = 0;
anc[i] = i;
f[i] = -1;
tree[i].clear();
que[i].clear();
}
}
int find(int a)
{
if (f[a] < 0)
{
return a;
}
return f[a] = find(f[a]);
}
void unions(int a, int b)
{
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
if (a != b)
{
if (f[a] > f[b])
{
f[b] += f[a];
f[a] = b;
}
else
{
f[a] += f[b];
f[b] = a;
}
}
}
void lca(int u)
{
int i, size;
size = tree[u].size();
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
lca(tree[u][i]);
unions(u, tree[u][i]);
anc[find(u)] = u;
}
visit[u] = 1;
size = que[u].size();
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (visit[que[u][i]] == 1)
{
num[anc[find(que[u][i])]]++;
}
}
}
int main()
{
char a[100], b[100];
int n, i, j, u, v, m;
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
set(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d:(%d)", &u, &m);
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &v);
tree[u].push_back(v);
in[v]++;
}
}
scanf("%d", &m);
while (m--)
{
scanf(" (%d %d)", &u, &v);
que[u].push_back(v);
que[v].push_back(u);
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (in[i] == 0)
{
lca(i);
break;
}
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (num[i])
{
printf("%d:%d\n", i, num[i]);
}
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
]]>
Description
Input
* Line 2+M: A single integer, K. 1 <= K <= 10,000
* Lines 3+M..2+M+K: Each line corresponds to a distance query and contains the indices of two farms.
Output
Sample Input
7 6
1 6 13 E
6 3 9 E
3 5 7 S
4 1 3 N
2 4 20 W
4 7 2 S
3
1 6
1 4
2 6
Sample Output
13
3
36
йўҳж„ҸеQҡз»ҷеҮЮZёҖӢӮү| ‘еQҢе…¶е®һжҳҜдёӘеӣҫгҖӮжұӮеҮЮZёӨзӮ№д№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„жңҖзҹӯи·қјӣ…RҖ?br>#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define maxn 600010
int son[maxn], loc[maxn], dis[maxn], sw[maxn], indegree[maxn], th;
struct T
{
int e, d;
}rmq[maxn*2][30];
struct F
{
int u, v, w, next;
}fn[maxn * 2];
void set(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
son[i] = 0;
indegree[i] = 0;
dis[i] = -1;
loc[i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
fn[i].next = 0;
}
}
void link(int u, int v, int w)
{
/*
ж ‘зҡ„йҒҚеҺҶеQҢиҝҷдёӘеҫ—и®оCҪҸгҖӮиҠӮзңҒз©әй—ҙгҖ?br> */
th++;
fn[th].u = u, fn[th].v = v, fn[th].w = w, fn[th].next = son[u], son[u] = th;
th++;
fn[th].u = v, fn[th].v = u, fn[th].w = w, fn[th].next = son[v], son[v] = th;
}
/*
йҖҡиҝҮжҗңзғҰжқҘз”ҹжҲҗж ‘зҡ„йҒҚеҺҶиҠӮзӮ?br>*/
void dfs(int d, int u, int f, int sd)
{
int v, i;
th++;
if (loc[u] == -1)//еҸӘиҝҳжІЎеҮәзҺ°иҝҮзҡ„иҠӮзӮ№еңЁйҒҚеҺҶдёӯзҡ„ж—үҷ—ҙжҲ»IјҲдҪҚзҪ®еQ?/span>
{
loc[u] = th;
dis[u] = sd;//и·қзҰ»жҳҜеҸ еҠ зҡ„гҖ?/span>
}
rmq[th][0].e = u;
rmq[th][0].d = d;
for (i = son[u]; i; i = fn[i].next)
{
if (fn[i].v != f)
{
dfs(d + 1, fn[i].v, u, sd + fn[i].w);
th++;
rmq[th][0].e = u;
rmq[th][0].d = d;
}
}
}
void build (int n)
{
int c = log((double)n) / log(2.0), i, j, m;
for (i = 1; i <= c; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
m = j + (1 << (i - 1));
if (m > n)
{
rmq[j][i] = rmq[j][i-1];
}
else
{
if (rmq[j][i-1].d <= rmq[m][i-1].d)
{
rmq[j][i] = rmq[j][i-1];
}
else
{
rmq[j][i] = rmq[m][i-1];
}
}
}
}
}
int query(int u, int v)
{
if (loc[u] > loc[v])
{
u ^= v;
v ^= u;
u ^= v;
}
int i = loc[u], j = loc[v];
int len = j - i + 1;
int c = log((double)len) / log(2.0);
int m = j - (1 << c) + 1;
int ancestor;
if (rmq[i][c].d <= rmq[m][c].d)
{
ancestor = rmq[i][c].e;
}
else
{
ancestor = rmq[m][c].e;
}
return dis[u] + dis[v] - 2 * dis[ancestor];
}
int main()
{
char c[2];
int n, m, u, v, w, k, t, i;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
set(n);
th = 0;
while (m--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%s", &u, &v, &w, c);
link(u, v, w);
}
th = 0;
dfs(0, 1, 0, 0);
build (2 * n - 1);
scanf("%d", &k);
while (k--)
{
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
printf("%d\n", query(u, v));
}
return 0;
}
]]>
Description
You are given a sequence of n integers a1 , a2 , ... , an in non-decreasing order. In addition to that, you are given several queries consisting of indices i and j (1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n). For each query, determine the most frequent value among the integers ai , ... , aj.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers n and q (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 100000). The next line contains n integers a1 , ... , an (-100000 ≤ ai ≤ 100000, for each i ∈ {1, ..., n}) separated by spaces. You can assume that for each i ∈ {1, ..., n-1}: ai ≤ ai+1. The following q lines contain one query each, consisting of two integers i and j (1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n), which indicate the boundary indices for the
query.
The last test case is followed by a line containing a single 0.
Output
For each query, print one line with one integer: The number of occurrences of the most frequent value within the given range.
Sample Input
10 3
-1 -1 1 1 1 1 3 10 10 10
2 3
1 10
5 10
0
Sample Output
1
4
3
йўҳж„ҸеQҡжҹҘжү‘ЦҢәй—ҙеҶ…ж•°еҮәзҺ°жңҖеӨҡзҡ„ӢЖЎж•°
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define maxn 100010
#define Max(a, b) a > b ? a : b
int num[maxn], v[maxn], rq[maxn][20];
void build(int n)
{
int i, j, m, r = n, c = log((double)n) / log(2.0);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
rq[i][0] = v[i];
}
for (i = 1; i <= c; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= r; j++)
{
m = j + (1 << (i - 1));a
if (m <= r)
{
rq[j][i] = Max(rq[j][i-1], rq[m][i-1]);
}
else
{
rq[j][i] = rq[j][i-1];
}
}
}
}
int rmq(int l, int r)
{
int len = r - l + 1;
int k = log(double(len)) / log(2.0);
int m = r - (1 << k) + 1;
return Max(rq[l][k], rq[m][k]);
}
int query(int l, int r)
{
int left, i;
if (num[l] == num[r])
{
return r - l + 1;
}
for (i = l; ; i++)
{
if (v[i] == 1)
{
left = i - l;
break;
}
}
return Max(left, rmq(i, r));
}
int main()
{
int n, m, i, l, r;
while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) == 2)
{
scanf("%d", &num[1]);
v[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
if (num[i] == num[i-1])
{
v[i] = v[i-1] + 1;
}
else
{
v[i] = 1;
}
}
build(n);
while (m--)
{
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
printf("%d\n", query(l, r));
}
}
return 0;
}
]]>
Description

In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
Output
Sample Input
2
16
1 14
8 5
10 16
5 9
4 6
8 4
4 10
1 13
6 15
10 11
6 7
10 2
16 3
8 1
16 12
16 7
5
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 5
3 5
Sample Output
4
3
йўҳж„ҸеQҡз»ҷеҮәж ‘зҡ„з»“жһ„пјҢй—®дёӨиҠӮзӮ№зҡ„жңҖҳq‘е…¬е…ЮqҲ¶иҠӮзӮ№гҖ?br>д»Јз ҒеQ?br>#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#define maxn 10001
using namespace std;
int visit[maxn], indegree[maxn], f[maxn], ancestor[maxn];
vector<int> tree[maxn], que[maxn];
void init(int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
tree[i].clear();
que[i].clear();
f[i] = -1;
visit[i] = 0;
indegree[i] = 0;
ancestor[i] = i;
}
}
int find(int a)
{
if (f[a] < 0)
{
return a;
}
return f[a] = find(f[a]);
}
void unions(int a, int b)
{
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if (a != b)
{
if (f[a] > f[b])
{
f[b] += f[a];
f[a] = b;
}
else
{
f[a] += f[b];
f[b] = a;
}
}
}
void lca(int u)
{
int i, size;
size = tree[u].size();
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
lca(tree[u][i]);
unions(u, tree[u][i]);
ancestor[find(u)] = u;
/*еҜ№дәҺеӨ„зҗҶҳqҮзҡ„еӯ©еӯҗеQҢе…¶јң–е…ҲиҰҒж”№дёәеҪ“еүҚиҠӮзӮ№пјҢдҝқиҜҒҳqҷжЈөж•°зҡ„йҒҚеҺҶйҖ»иҫ‘еQ?br> еӣ дШ“тq¶жҹҘйӣҶзҡ„еҗҲеЖҲжҳҜжҢүжқғеҖЖDҖҢйқһйҒҚеҺҶҷеәеәҸеҗҲеЖҲзҡ?йҖҡиҝҮтq¶жҹҘйӣҶй«ҳж•ҲиҺ·еҫ—еӯҗж ‘йӣҶеҗҲзҡ„з«ҜеҸЈеQҢеңЁйҖҡиҝҮҳqҷз«ҜеҸЈиҺ·еҫ?br> иҜҘеӯҗж ‘еңЁҳqҷдёӘж—үҷ—ҙҢDлҠҡ„зңҹжӯЈжңҖҳq‘зҲ¶иҠӮзӮ№еQҢеҰӮеӣҫдёӯзҡ?еңЁеЖҲжҹҘж ‘дёӯдјҡиў«еҪ’тq¶дШ“6зҡ„еӯ©еӯҗпјҢеӣ дШ“жқғеҖјзҡ„й—®йўҳ*/
}
visit[u] = 1;
size = que[u].size();
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (visit[que[u][i]] == 1)
{
printf("%d\n", ancestor[find(que[u][i])]);
return;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n, t, i, u, v;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
init(n);
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
tree[u].push_back(v);
indegree[v]++;
}
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
que[u].push_back(v);
que[v].push_back(u);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (indegree[i] == 0)
{
lca(i);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
]]>
f[i][j]иЎЁзӨәд»Ҙiдёшҷ“vзӮҡw•ҝеәҰдШ“2^jзҡ„жңҖеҖ№{Җ?/span>
f[i][j] = rmq(f[i][j-1], f[i + 2 ^ (j-1)][j-1];зӣёеҪ“дәҺжҠҠҫUҝж®өеҲҶжҲҗзӣёзӯүзҡ„е·ҰеҸідёӨҢDөеҗҲтq¶жұӮrmqгҖӮдҪҶҳqҷеҫ—и®©зәҝҢDөй•ҝеәҰжҳҜ2зҡ„е№ӮӢЖЎгҖ?/span>
жҹҘиҜўж—УһјҢдҫӢеҰӮf[1еQ?] = f[1][2] + f[5][1] + f[7][0];дёәO(logn),f[1, 7]еҜ№еә”дәҺж•°ҫl„дёӯзҡ„еҢәй—?/span>
дёЮZәҶеҠ еҝ«жҹҘиҜўеQҢеҸҜдҪҝf[1еQ?] = f[1][2] + f[4][2];дёәO(1)еQҢиҝҷйҮҢз”Ё2=еQ?^k <= 7еQүkзҡ„жңҖеӨ§еҖ? - 2^2 + 1 дё?еQҢеҚіи®?еҗ‘е·ҰҝUХdҠЁ2^2 - 1дёӘдҪҚеQ?^k = 1 << k;жіЁж„ҸеQҡдҫӢеҰӮз»ҷеҮәn=7еQҢеҲҷf[4][2]жҳҜжұӮеҜ№еә”дәҺ[4, 8]зҡ„rmqеQҢиҖҢf[4, 8] = f[4, 7],жүҖд»ҘиҰҒеҜТҺӯӨҳqӣиЎҢйў„еӨ„зҗ?и®©еҸіеҢәй—ҙзҡ„еҖЖD¶…ҳqҮnзҡ„дШ“еҸӣ_Ңәй—ҙдШ“nж—¶зҡ„еҖы|јҢҳqҷж ·жүҚиғҪеҠ еҝ«жҹҘиҜўеQҢеҚіеӨҡеўһеҠ дәҶдёҖдәӣж–№дҫҝжҹҘиҜўзҡ„ж•°жҚ®гҖӮжңҖеӨ§е·ҰҝUАLҳҜk = log2(n),еҸҜиЎЁҪCәзҡ„жңҖеӨ§и“vе§ӢзӮ№жҳ? << k,еҲҷf[i][j]иЎЁзӨәзҡ„еҸіеҢәй—ҙзҡ„жңҖеӨ§еҖйgШ“
(1 << k) + (1 << k) = 1 << (k + 1) = 2 ^ (log2(n) + 1),жҸҗдҫӣҳqҷдёӘж•°жҚ®ж—¶иғҪҫlҷеҮәдҪ•ж—¶еҫ—з©әй—ҙ[n + 1][log2(n) + 1 + 1]гҖ?/span>
д»Јз ҒеQ?/span>
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < math.h >
#define maxn 50010
#define Min(a, b) a < b ? a : b
#define Max(a, b) a > b ? a : b
struct t
{
int min, max;
}map[maxn][ 20 ];
void build ( int n)
{
int i, j, m, r = n, c = log(( double )n) / log( 2.0 );
for (i = 1 ; i <= c; i ++ )
{
for (j = 1 ; j <= r; j ++ )
{
m = j + ( 1 << (i - 1 )); // еҸӣ_ҚҠйғЁеҲҶзҡ„и“vе§ӢеҖ?/span>
if (m <= r)
{
map[j][i].min = Min(map[j][i - 1 ].min ,map[m][i - 1 ].min);
map[j][i].max = Max(map[j][i - 1 ].max, map[m][i - 1 ].max);
}
else // й•ҝеәҰӯ‘…еҮәnзҡ„пјҢһ®ұеҪ“жҳҜjиөпLӮ№зҡ„жңҖеҗҺдёҖдёӘз»ҲзӮ№зҡ„rmqгҖӮе®һзҺ°иҝҷжӯҘиғҪдҪҝжҹҘиҜўдШ“O(1).
{
map[j][i].min = map[j][i - 1 ].min;
map[j][i].max = map[j][i - 1 ].max;
}
}
}
}
int query( int l, int r)
{
int len = r - l + 1 ;
int k = log(( double )len) / log( 2.0 );
int m = r - ( 1 << k) + 1 ;
int min = Min(map[l][k].min, map[m][k].min);
int max = Max(map[l][k].max, map[m][k].max);
return max - min;
}
int main()
{
int n, m, i, l, r;
scanf( " %d%d " , & n, & m);
for (i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++ )
{
scanf( " %d " , & map[i][ 0 ].min);
map[i][ 0 ].max = map[i][ 0 ].min;
}
build (n);
while (m -- )
{
scanf( " %d%d " , & l, & r);
printf( " %d\n " , query(l, r));
}
return 0 ;
}
]]>